Washington University School of Medicine
-
A readily available sleep aid has been shown to have a surprising side effect on brain health, seemingly protecting the organ from the buildup of the tau protein – a key biomarker in the development of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's.
-
A long-term trial has found that a discontinued drug halved the onset of a genetic form Alzheimer's, from all but 100% to 50%. Buoyed by the results, scientists are now trialing anti-amyloid medication as a preventative for all types of the disease.
-
A simple little sticker could soon be saving the lives of patients recovering from gastrointestinal surgery. The clever device is designed to detect the presence of leaking digestive fluids sooner than otherwise possible.
-
Chitin, which provides crucial exoskeletal structure and protection to soft-bodied arthropods such as crustaceans, spiders and insects, may have a surprising role in switching up human metabolism in the gut, helping to fight weight gain and obesity.
-
A 31-year-old woman desperately needed a heart transplant to save her life, but doctors knew her body would reject the organ. So they took an unusual approach: they also replaced her healthy liver. The procedure was a groundbreaking success.
-
We’re getting closer to being able to induce hibernation on demand in humans for surgery or space travel. Scientists have now demonstrated a way to induce a hibernation-like state in mice and rats using non-invasive ultrasound pulses to the brain.
-
While opioids are among the most powerful painkillers, they're also highly addictive, which makes them hard to get. A new finding may offer hope to pain patients in the form of powerful drugs that lack the most severe side effects of current options.
-
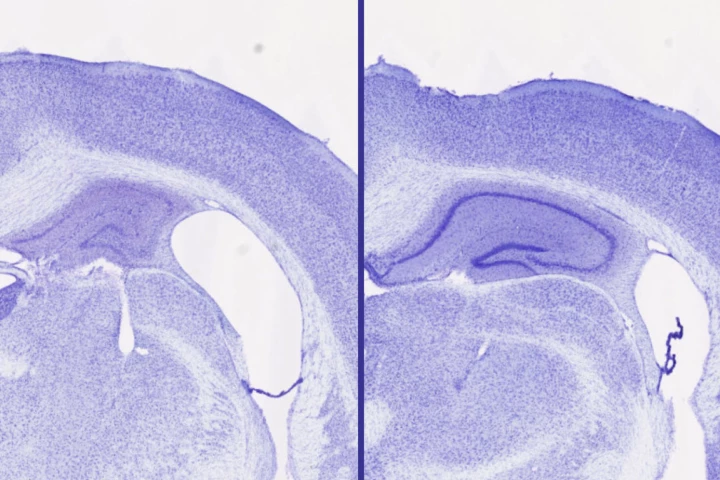
A common sleeping pill showed promise in combating the substances that lead to the harmful tangles and plaques in the brain that contribute to Alzheimer's disease, but larger, more comprehensive studies are needed to confirm the results.
-
In the first study to investigate the effect of repeat SARS-CoV-2 infections on a person's general health researchers have found COVID reinfections can increase one's risk of neurological diseases, diabetes, lung problems and heart disease.
-
Scientists have identified a protein implicated in the progression of Alzheimer's disease that appears highly regulated by the circadian rhythm, helping them join the dots between the two and providing a potential new therapeutic target.
-
A new study led by researchers from the Stanford School of Medicine suggests low levels of a hormone called vasopressin, measured in three-month-old babies, may serve as a predictive biomarker of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in later childhood.
-
New research suggests malnutrition in children can be better treated by therapeutic foods designed to boost and repair the gut microbiome. A clinical trial targeting malnourished children in Bangladesh revealed a newly developed therapeutic food is superior to conventional supplements.
Load More