Yale
-
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers zoomed in on PTSD at the single-cell level to better understand how it affects the brain. The findings revealed how trauma can lead to specific molecular changes in some brain cells.
-
Why don’t we remember specific events during those crucial first few years, when our brains worked overtime to learn so much? A new Yale study finds evidence that we do form memories, but can’t retrieve them.
-
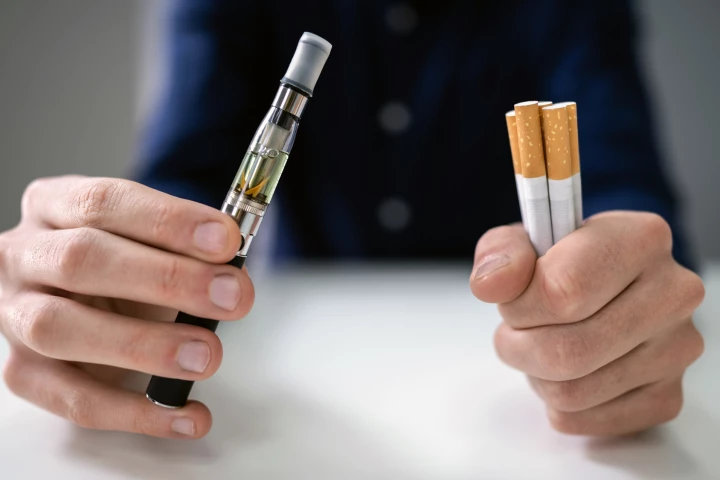
With the rise of vaping, a big question has been whether drugs that help cigarette smokers quit will work for e-cigarette users. The first US trial using an existing drug to help vapers quit has shown they're effective, even without ongoing counseling.
-
The biggest tragedy of pet ownership is that they just don’t live long enough. Thankfully scientists are working on that, with a new cancer vaccine for dogs that almost doubles their survival rates in the face of certain types of the disease.
-
White blood cell numbers can be cut by health conditions or treatments like chemotherapy. Yale scientists have now discovered a molecule that can be given to quickly boost their numbers back up, to help fight off infections without antibiotics.
-
Exercise is usually a good thing but for many long COVID patients it can often make their condition worse. Two new studies are shedding light on this counter-intuitive phenomenon, finding distinct physiological abnormalities in long COVID patients.
-
Research has found that the brains of people with PTSD process traumatic personal memories differently from sad ones. The findings suggest traumatic memories activate a distinct pathway, which may be critical to PTSD treatment.
-
Researchers have found that when used on monkeys, an experimental drug slowed the process that leads the tau protein to aggregate into neuron-damaging tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. The next step is to develop a drug for use in humans.
-
A phase 3 clinical trial has shown that a drug called teplizumab can slow progression of type 1 diabetes in children and teenagers with a recent diagnosis. The trial’s success helps expand options for patients and relieve some burdens of the disease.
-
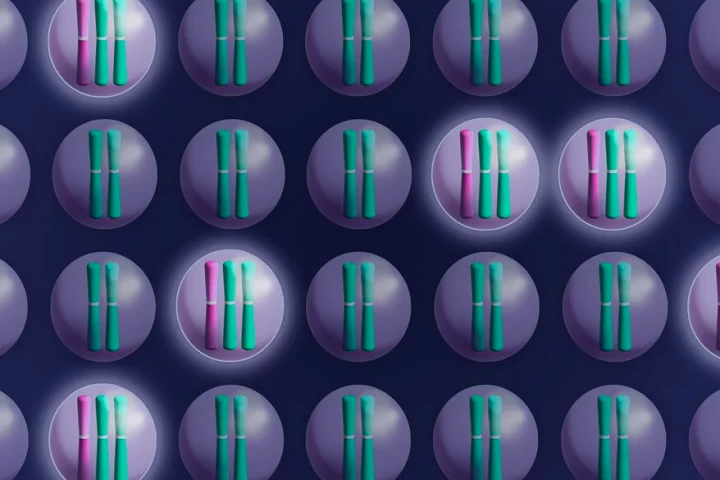
Yale scientists have discovered a new potential treatment avenue to fight cancer. Using CRISPR gene-editing, the team eliminated extra chromosomes from cancer cells and found that they could no longer grow out of control.
-
While the ‘move more, eat less’ mantra is prevalent, more is being discovered about the complex brain-gut link in obesity and weight loss. Now, a new study suggests faulty ‘reward’ dopamine release may be fueling poor nutrition and chronic overeating.
-
A groundbreaking project has seen hundreds of scientists across the world uncover many mysteries of the evolution of mammals, work that may help us understand why humans are unique and what genetic changes may be key to some of our unique diseases.
Load More