You'd think that a planet with permanent day and night sides would be totally inhospitable. Without a sun to warm it up, the dark side would be freezing cold all the time. And with no respite from the solar onslaught, the light side would be scorching hot. But a new study suggests that exoplanets with this very predicament might in fact be habitable under two out of three possible climate types.
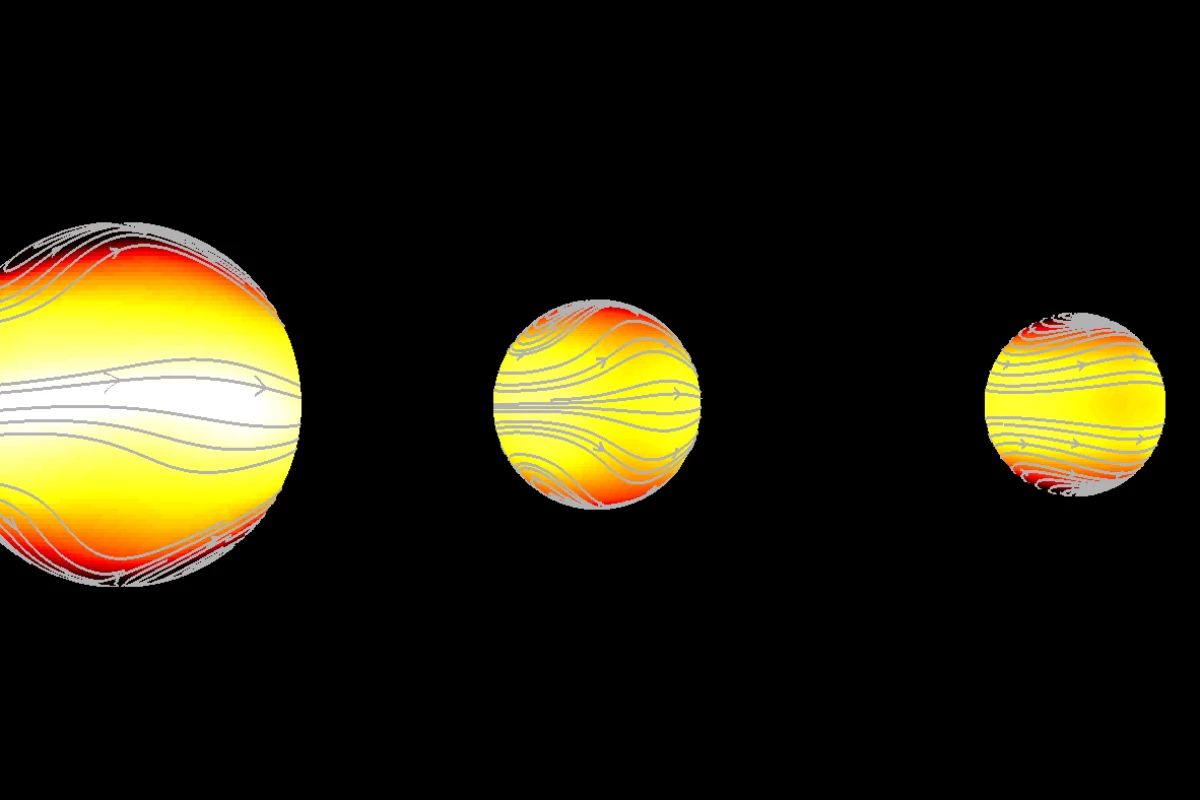
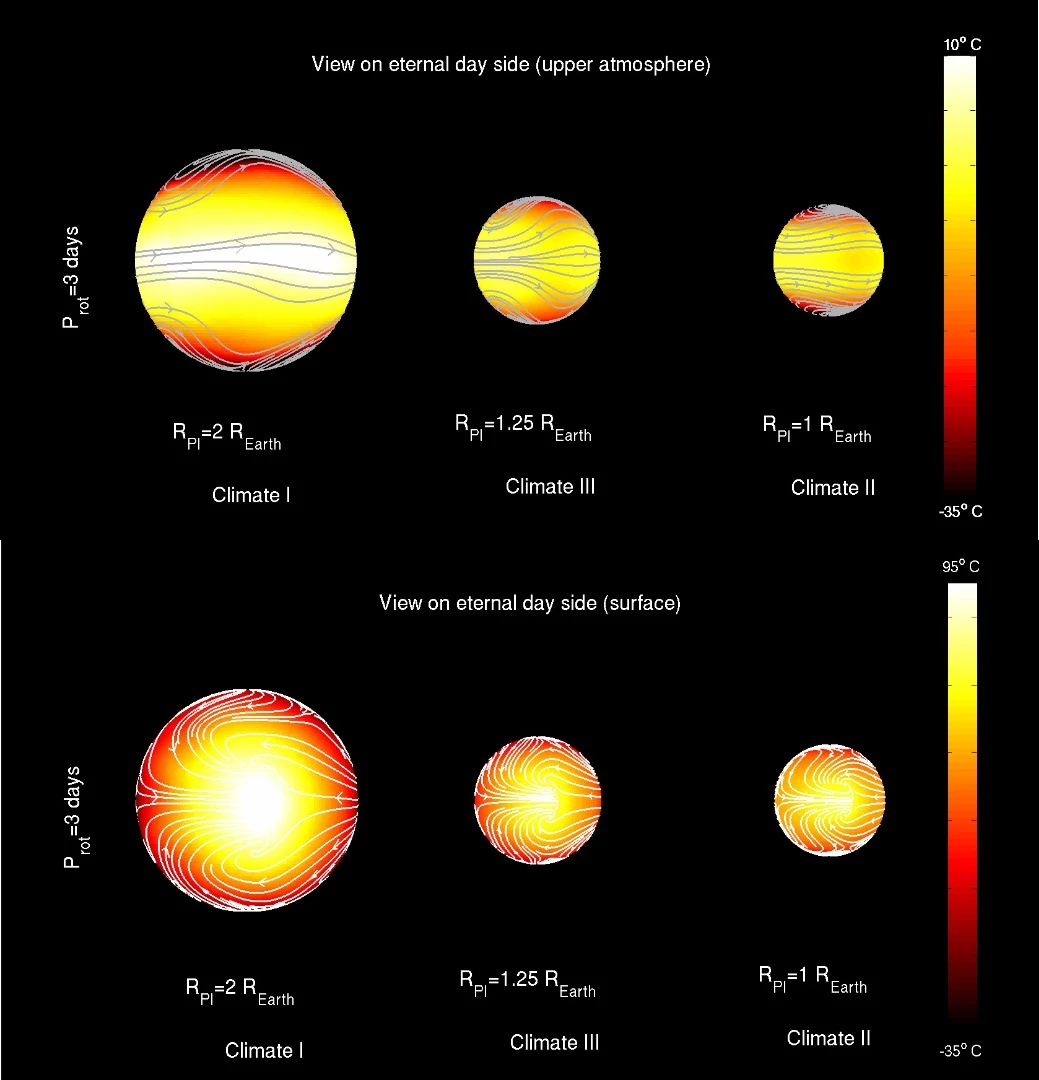
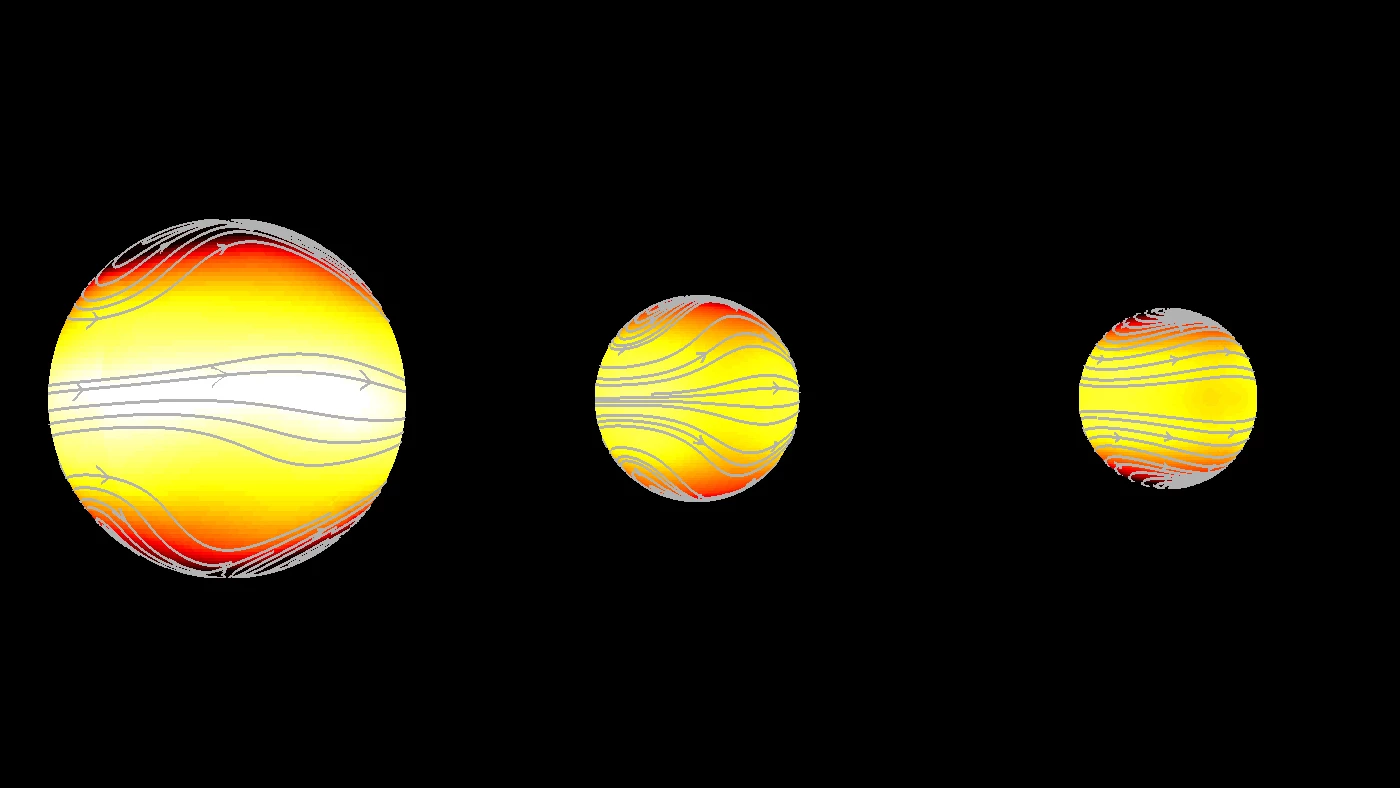
Using 3D models, scientists at KU Leuven in Belgium ran 165 climate simulations on exoplanets known to be "tidally locked" to their star. This means that their rotations are in sync with that of their star, so the same side always faces the it – like the way the same side of the Moon always faces the Earth.
For tidally locked exoplanets to be potentially habitable, they must have a functional planetary "air conditioning system" that balances surface temperatures across the light and dark sides. In one climate type uncovered by the simulations, this air conditioning system is overridden by an eastward wind jet (fast flowing air currents) that messes with circulation in the upper layers of the atmosphere along the equator and prevents heat transfer to the night side.
That only occurs on exoplanets with rotation periods under 12 days, however. The simulations showed that the rest have either two westward jets at high latitudes or a longitudinal "smearing" of the upper atmosphere hotspot across the substellar point (the point at which the star is in zenith, or directly overhead). Both of these other climate types leave the air conditioning system unaffected and thus make the surface potentially habitable.
The finding is valuable because tidally locked exoplanets usually orbit closely to their stars, and exoplanets that are close to their stars are not only easier for researchers to detect and observe but also more likely to contain liquid water than those with a wider orbit.
The study will also help in the tough task of sorting through the growing list of exoplanets discovered (now approaching 2000) to find ones that might be future homes for us humans. Even if they don't look like Earth, tidally locked exoplanets such as 2010 discovery Gliese 581g might just turn out to be viable for our future cosmic sprawl.
A paper describing the study was published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Source: KU Leuven