Last year, researchers from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, found that replacing up to 15% of the sand ordinarily used in concrete with waste coffee grounds made it 30% stronger. It's a case of killing two birds with one coffee bean: the production method not only reduces reliance on sand, a non-renewable resource, but also reduces the amount of organic waste sent to landfills, thereby reducing its contribution to greenhouse gas emissions.
Organic waste can’t be added directly to concrete because it decomposes over time, weakening the material. So, the researchers developed a low-energy process where the coffee grounds are heated at 350 °C (662 °F) without oxygen to create biochar.
We regularly report on potentially industry-changing developments in the materials space, but it’s not often that we see them put to practical use. RMIT has partnered with a local Victorian government council, the Macedon Ranges Shire Council, to lay organic waste-enhanced concrete sidewalks (or 'footpaths' as they're called Down Under) in a world-first trial. Two types of concretes – one made with coffee biochar and one with wood chip biochar – were laid alongside standard concrete, which will act as a control.
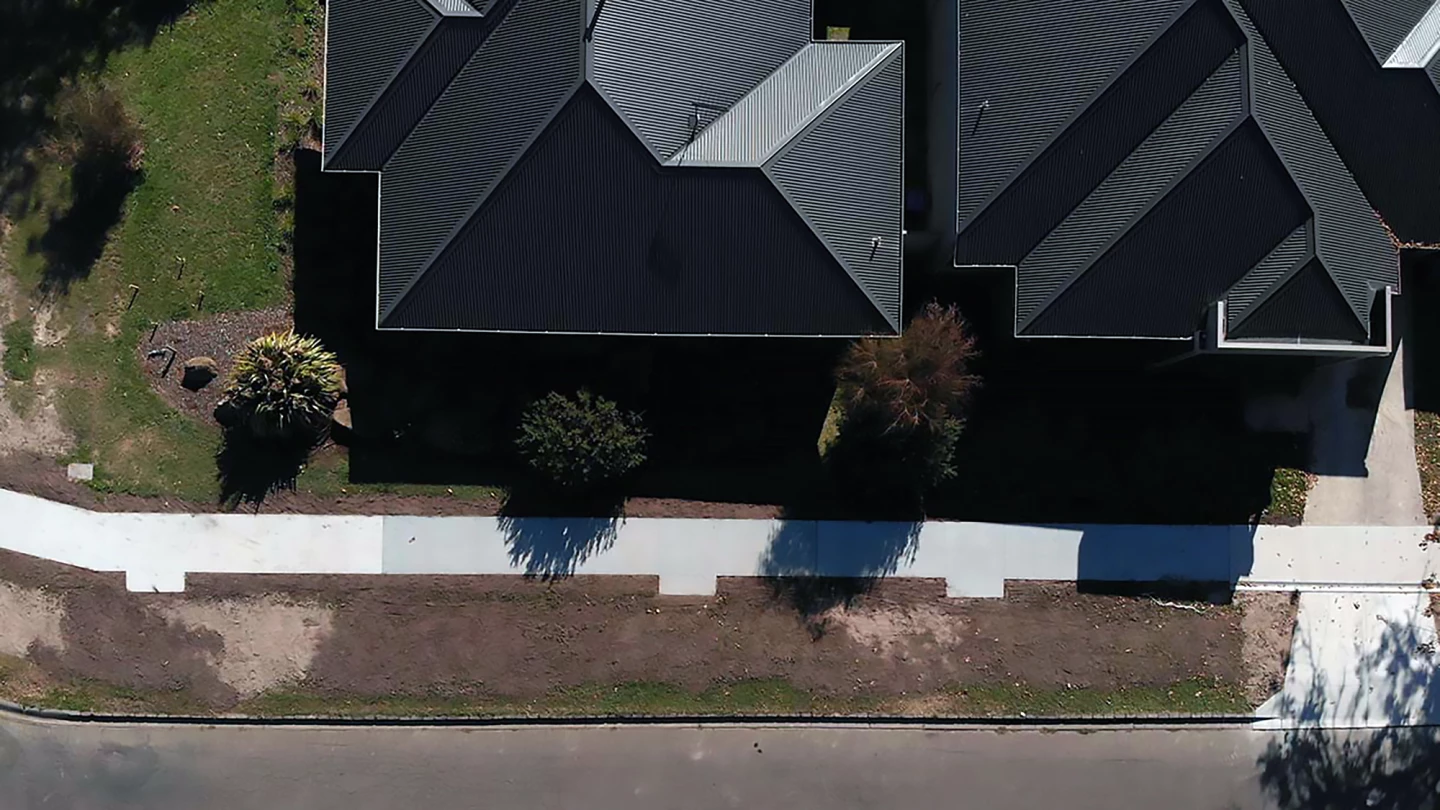

“We’re taking those experiments and putting them in ground and in the field today, we’re going to have people walking across the concrete that includes these products, and RMIT is going to be coming back and doing testing to see how they stand up,” said Shane Walden, the Council’s Director of Assets and Operations. “This not only helps improve the knowledge level of our contractors and our staff, but it also has lots of other benefits and benefits that are important to our community. This includes helping the environment, acting sustainably and, most importantly, reducing waste to landfill and having a circular economy.”
The researchers will roll out more of the innovative material based on how well it performs.
“We are currently working in the supply chain sector so that we can make this product into a mainstream product for commercial applications, and we’re not only looking into coffee – we’re expanding this into all forms of different organic waste,” said Rajeev Roychand, from RMIT’s School of Engineering. “Every biochar produced from a different organic material comes with varying composition, in addition to the difference in carbon content, particle size and absorbency, that can boost the performance of concrete in a range of ways.”
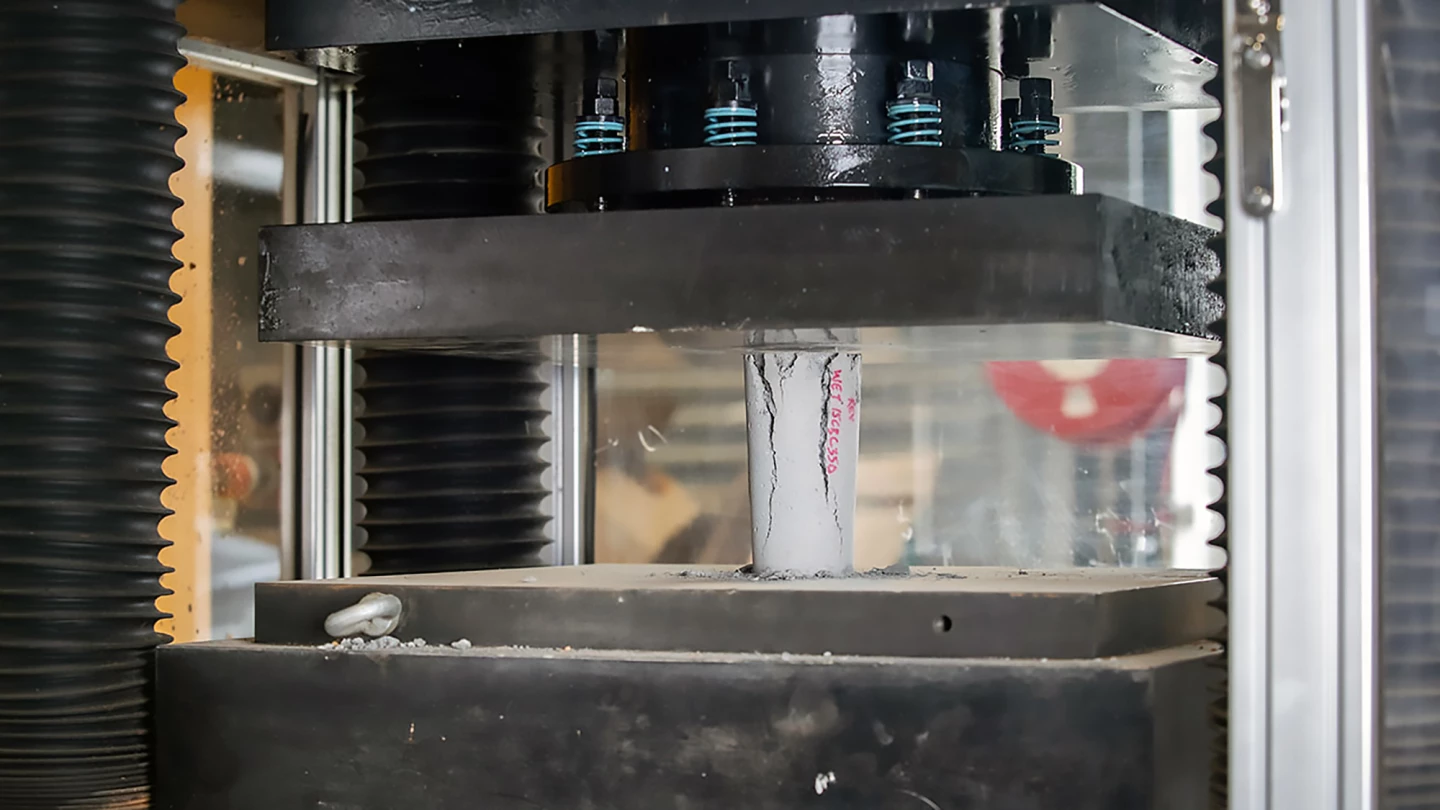
Using organic waste-enhanced concrete could mean construction cost savings.
“Our research creates a potential to even reduce the required cement content,” Roychand said. “Since we are achieving a 30% increase in strength for the coffee concrete, this could reduce the required cement content by as much as 10%, based on our previous experience.”
Source: RMIT









