For a few years now, scientists at Washington University have been working on techniques to turn stem cells into pancreatic beta cells as a way of addressing insulin shortages in diabetics. After some promising recent strides, the team is now reporting another exciting breakthrough, combining this technique with the CRISPR gene-editing tool to reverse the disease in mice.
The pancreas contains what are known as beta cells, which secrete insulin as a way of tempering spikes in blood-sugar levels. But in those with diabetes, these beta cells either die off or don’t function as they should, which means sufferers have to rely on diet and or regular insulin injections to manage their blood-sugar levels instead.
One of the ways scientists are working to replenish these stocks of pancreatic beta cells is by making them out of human stem cells, which are versatile, blank slate-like cells that can mature into almost any type of cell in the human body. The Washington University team has operated at the vanguard of this technology with a number of key breakthroughs, most recently with a cell implantation technique that “functionally cured” mice with diabetes.
The researchers are continuing to press ahead in search of new and improved methods, and this led them to the CRISPR gene-editing system, which itself has shown real promise as a tool to treat diabetes. The hope was that CRISPR could be used to correct genetic defects leading to diabetes, combining with the stem cell therapy to produce even more effective results.
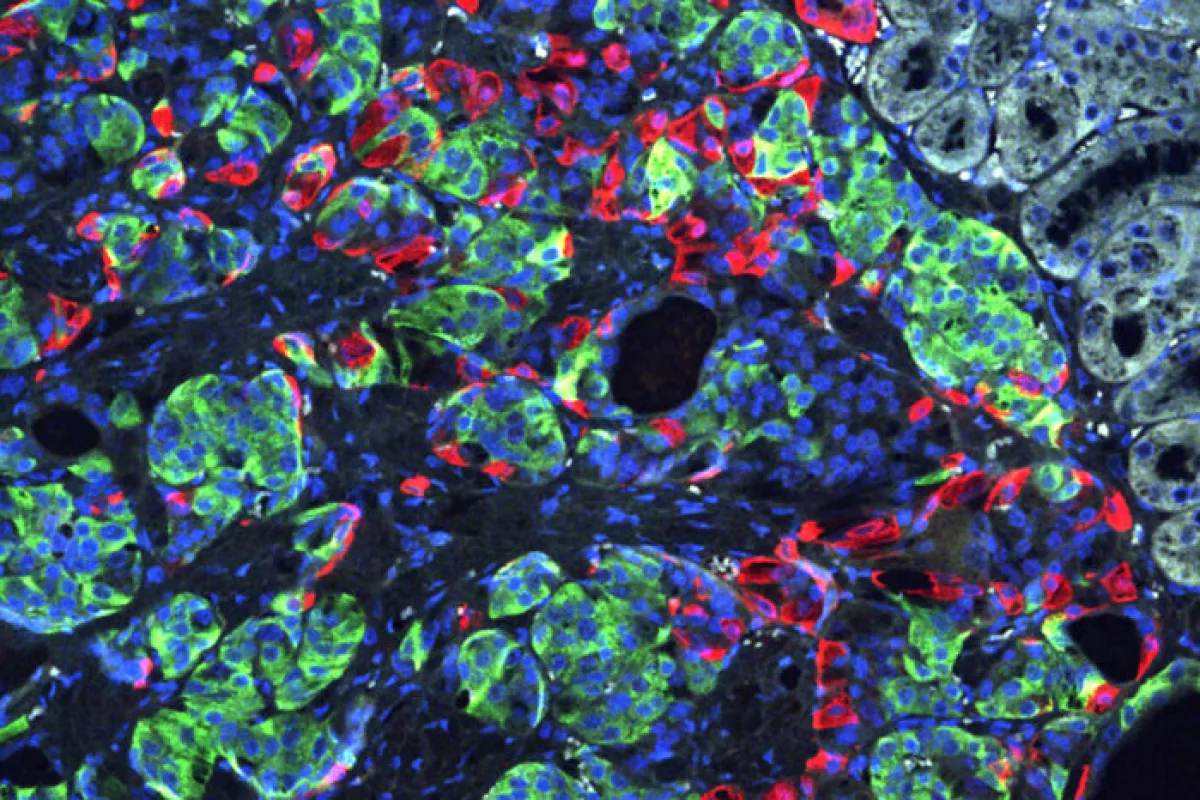
As a proof of concept, the scientists took skin cells from a patient with a rare genetic type of diabetes called Wolfram syndrome, which develops during childhood and typically involves multiple insulin injections each day. These skin cells were converted into induced pluripotent stem cells, which were in turn converted into insulin-secreting beta cells. But as an additional step, CRISPR was used to correct a genetic mutation that causes Wolfram syndrome.
These edited beta cells were then pitted against non-edited beta cells from the same batch in test tube experiments and in mice with a severe type of diabetes. The edited cells proved more efficient at secreting insulin and when implanted under the skin in mice, reportedly caused the diabetes to quickly disappear. The rodents that received the unedited beta cells remained diabetic.
“This is the first time CRISPR has been used to fix a patient’s diabetes-causing genetic defect and successfully reverse diabetes,” said co-senior investigator Jeffrey R. Millman. “For this study, we used cells from a patient with Wolfram syndrome because, conceptually, we knew it would be easier to correct a defect caused by a single gene. But we see this as a stepping stone toward applying gene therapy to a broader population of patients with diabetes.”
The researchers are now continuing to work on improving the beta cell production technique, which in the future could involve cells taken form the blood or even urine, rather than the skin. They believe that further down the track this therapy could prove useful in treating both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, by correcting mutations that arise from genetic and environmental factors, and possibly be used to treat other conditions, as well.
“We basically were able to use these cells to cure the problem, making normal beta cells by correcting this mutation,” said co-senior investigator Fumihiko Urano. “It’s a proof of concept demonstrating that correcting gene defects that cause or contribute to diabetes — in this case, in the Wolfram syndrome gene — we can make beta cells that more effectively control blood sugar. It’s also possible that by correcting the genetic defects in these cells, we may correct other problems Wolfram syndrome patients experience, such as visual impairment and neurodegeneration.”
The research was published in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Source: Washington University