NASA has announced the winners of its 3-D Printed Habitat Challenge Design Competition. The contest sought architectural concepts for how 3D printing might be used to create shelters on the Red Planet. The overall winner, Ice House, would be built using the planet's predicted abundant water supply.
More than 165 submissions to the competition, which was launched in May, were received by NASA. The 3-D Printed Habitat Challenge, of which the design competition is part, is ultimately aimed at contributing towards the development of new technologies for additive manufacturing using "local indigenous materials" in space and on Earth.
"The creativity and depth of the designs we’ve seen have impressed us," says NASA's Centennial Challenges Program Manager Monsi Roman. "These teams were not only imaginative and artistic with their entries, but they also really took into account the life-dependent functionality our future space explorers will need in an off-Earth habitat."
Ice House was designed by Team Space Exploration Architecture, and Clouds Architecture Office. It is based on NASA's "follow the water" approach to exploration. As water is a means of sustaining life and ice a potential building material, the team opted to locate at Alba Mons in Mars' northern hemisphere, where it is believed sub-surface water ice is plentiful.
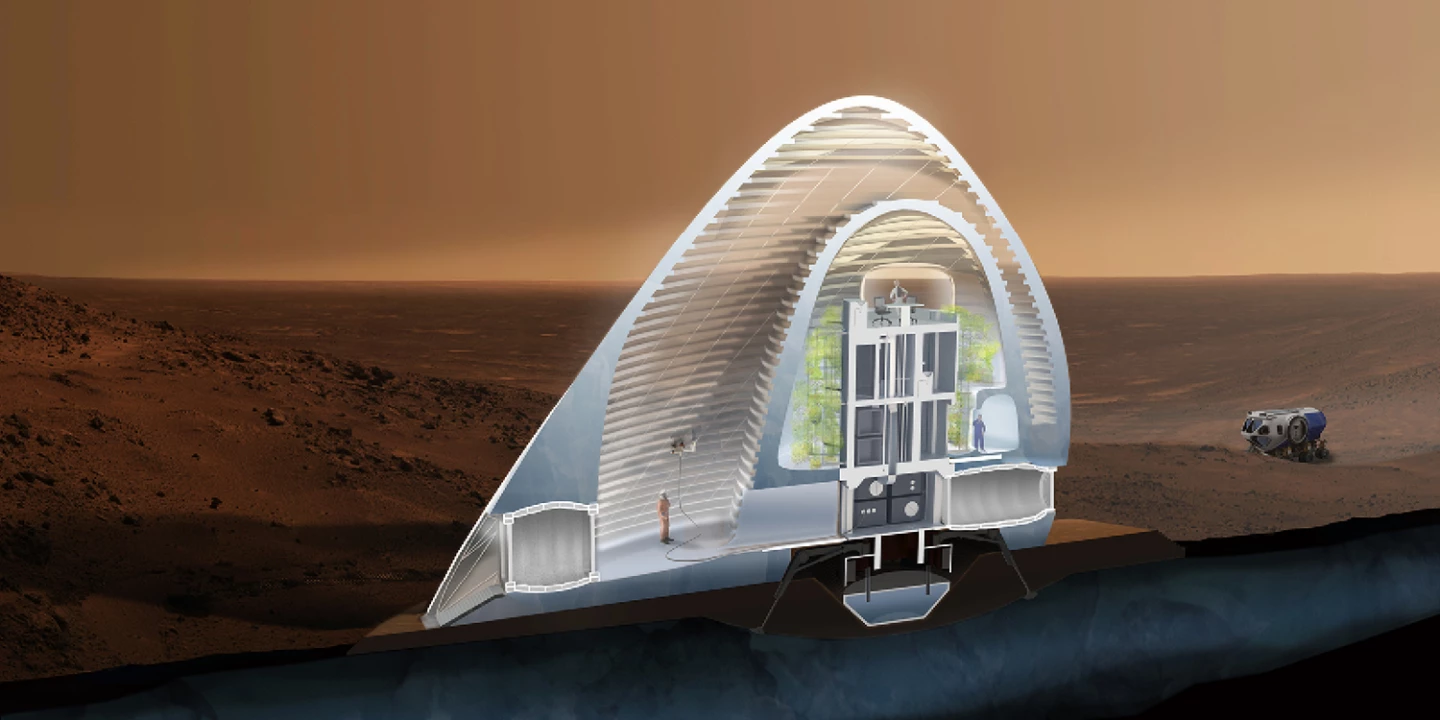
The proposal uses a lander as the basis of the shelter, containing both private and communal interior spaces. Once in situ, it would deploy an inflatable ETFE membrane to create an interstitial environment between the outside of the capsule and the Mars atmosphere. Rovers would then extract water from the ice below the surface at Alba Mons and apply it to form a protective skin on the inside of the inflatable environment.
Not only does the layer of ice provide protection from radiation in the outside atmosphere, it is also translucent and allows light into the habitat. By conditioning the environment within the inflatable section, it is proposed that the ice be kept frozen indefinitely and vegetation could be grown, which would help to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen.
The second place award of $15,000 went to Team Gamma, from architecture firm Foster + Partners. Its concept proposes using semi-autonomous robots to build a shelter using regolith (the loose soil and rocks found on the surface of Mars).
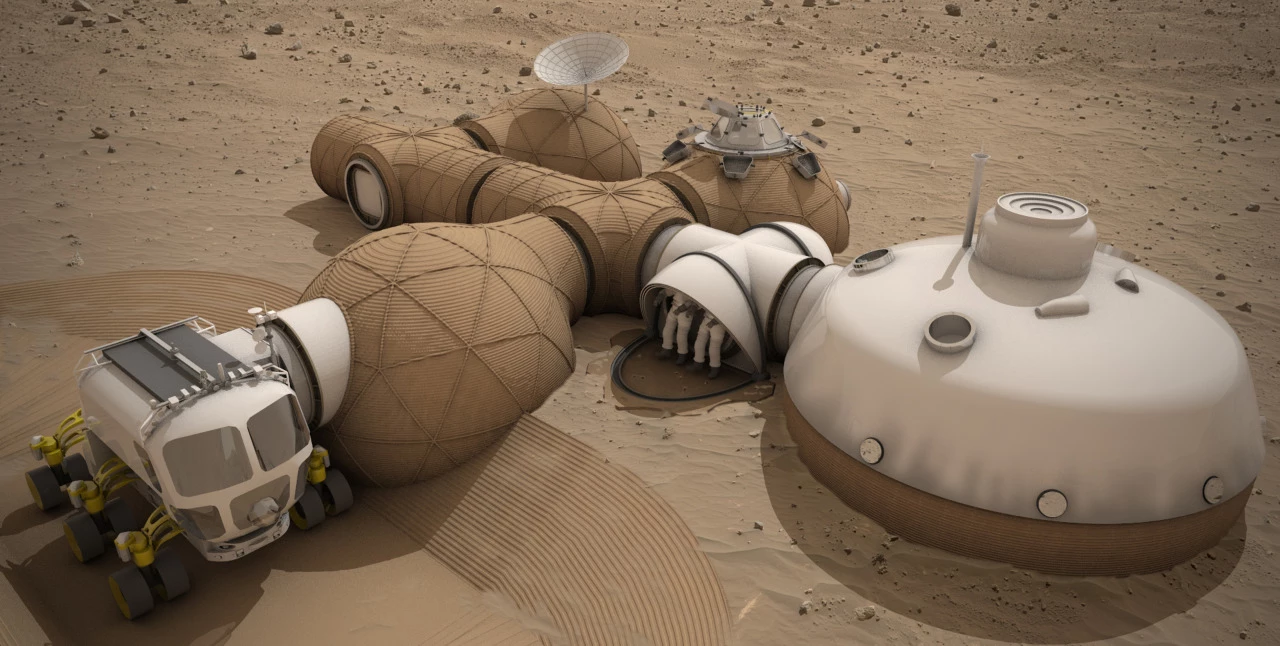
Finally, third place honors went to Team LavaHive. It proposes using construction rovers with inflatable attachment sections as the basis for the shelter. Once inflated, the sections would be covered in "lava-casted" regolith to create a protective layer. This approach would be used to create a number of adjacent shelters with adjoining corridors.
Teams were judged on many factors, including architectural concept, design approach, habitability, innovation, functionality, Mars site selection and 3D print constructability. The highest ranked 30 submissions, including the three winners, were displayed at the New York Maker Faire on Sunday, Sep. 27.
Source: NASA
















