antibodies
-
Scientists have developed a nasal 'molecular shield' that disarms pollen, blocking allergic reactions fast without the use of drugs. This non-invasive method to effectively silence hay fever could be a game changer for around 81 million Americans.
-
Over the course of 18 years, a truck mechanic from Wisconsin injected himself with snake venom hundreds of times. His actions were considered stunts by some over those years, but his blood has just helped lead the way toward a universal antivenom.
-
Scarring of heart tissue can be slowed but not stopped, and can lead to heart failure. But a new study has shown that an existing immunotherapy could stop scar tissue formation after heart attacks.
-
One dose of a new treatment, delivered by nasal spray, clears away build-ups of the toxic tau protein associated with Alzheimer’s disease from inside brain cells, improving memory, according to new research. It paves the way for new treatments for the debilitating disease.
-
Measles is on the rise, attributable to the anti-vaccination movement and exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Researchers have identified a new way of tackling one of the most contagious viruses around, offering protection for those at greatest risk.
-
A promising new drug could prevent and even reverse the onset of type 1 diabetes. The experimental monoclonal antibody drug was found to act like a shield to protect insulin-producing cells from damage and even extended lifespan in some cases.
-
The biggest tragedy of pet ownership is that they just don’t live long enough. Thankfully scientists are working on that, with a new cancer vaccine for dogs that almost doubles their survival rates in the face of certain types of the disease.
-
A drug used to treat asthma has been shown to substantially reduce the risk of potentially life-threatening reactions in people aged one and older with multiple common food allergies, including peanuts, following accidental exposure.
-
A universal snake-bite antivenom is within reach, with scientists making an antibody that protects against lethal strikes from a range of elapids. No snakes or ‘donor animals' were needed to produce the antivenom, making it sustainable and scalable.
-
Researchers found that getting a multidose vaccine in different arms may improve the body’s immune response to the vaccine by up to four-fold. While they exclusively looked at the COVID-19 vaccine, they suspect this effect may be seen with others.
-
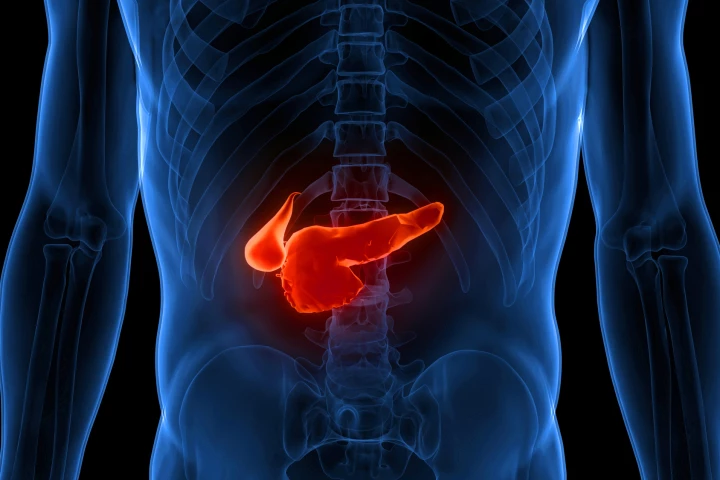
Researchers have used radioactive monoclonal antibodies to find and destroy a particularly lethal form of pancreatic cancer. The combination of diagnostics and therapeutics could lead to earlier detection and more effective treatment of the disease.
-
Researchers have found that an intranasal drug, currently being tested as an MS treatment, reduced brain inflammation and improved cognition in mice with Alzheimer’s disease, independent of the amount of beta-amyloid plaques present.
Load More