Bacteria
-
A new antibiotic to relieve stubborn urinary tract infections and a blood-clot dissolving treatment for acute ischemic stroke will be commercially available in the coming months. It's been nearly three decades since adjacent drugs have hit the market.
-
It's never a good thing, when a bacterial biofilm forms on the surface of a medical implant. There could soon be a new way of eradicating such films, however, using tiny remote-control liquid-bodied robots.
-
In seeking new antibiotic sources, researchers have turned to an unlikely source: a whiffy frog known as Odorrana andersonii. By unclumping a compound it produces naturally, they've found a potential gut-friendly ally in the fight against superbugs.
-
Scientists have made a major breakthrough in the accuracy and speed at which serious and often deadly pathogen infections can be diagnosed and treated. Often, this is time that is critically important in saving a patient's life.
-
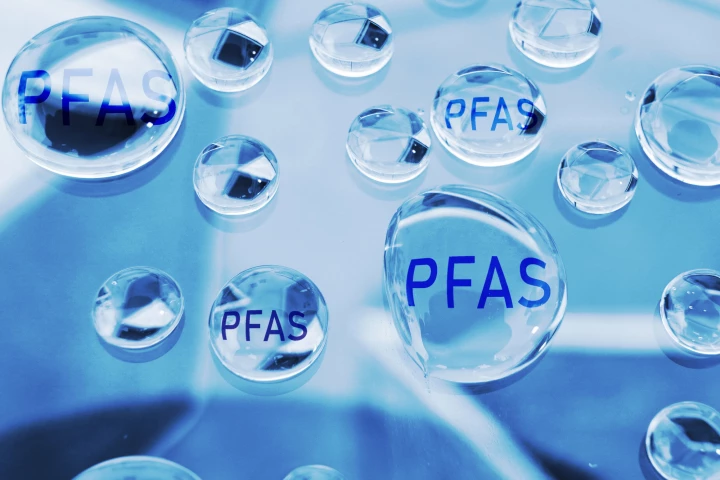
Toxic ‘forever chemicals’ are increasingly showing up in the environment, our food and drinking water, and our bodies. But we might have a new weapon: scientists have identified a bacterium that can eat these chemicals, as well as their byproducts.
-
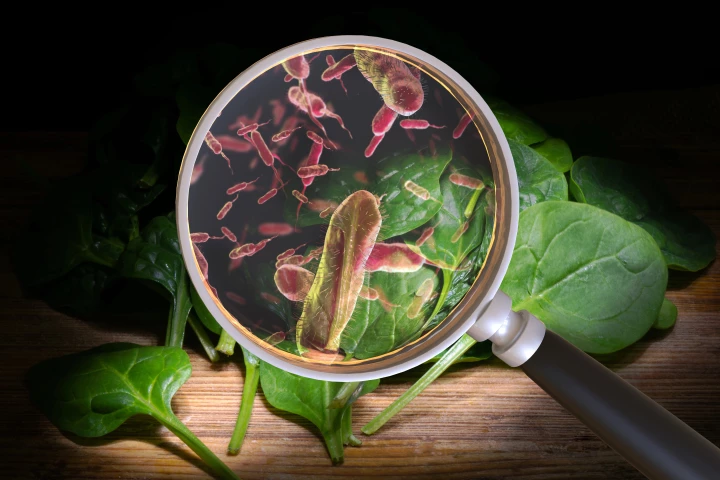
We've almost all been hit with a horror stomach bug. At best, it's a 24-hour nightmare, and at worst it's deadly. But huge strides are being taken towards the first Salmonella and norovirus vaccines, which could make severe illness a distant memory.
-
If you were given a choice of vaccine delivery method, would you rather a needle or a skin cream? Thought so. Well, the latter might be a viable option soon, as Stanford scientists have used a topical cream to strongly vaccinate mice against tetanus.
-
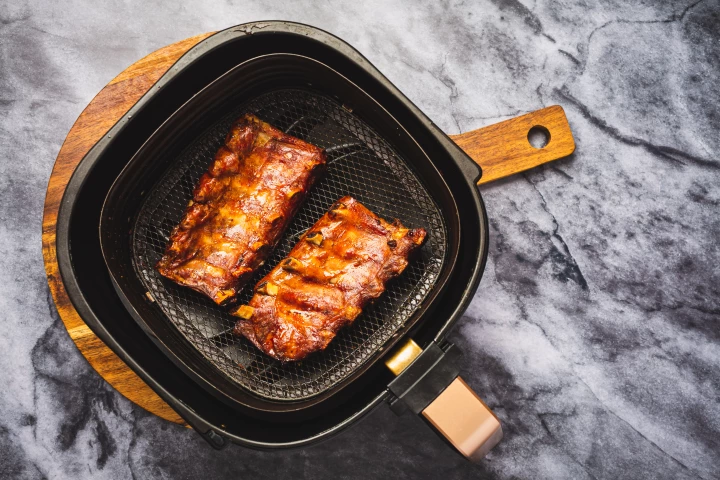
It's nearly 15 years since the first modern air fryer hit the market, but food companies and consumers are still catching up when it comes to food safety and these game-changing kitchen gadgets. Experts share what needs to be done to safeguard health.
-
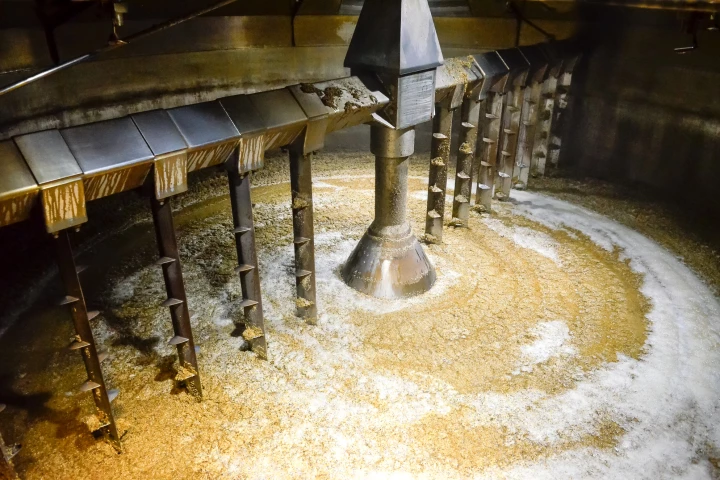
In Kentucky, bourbon demand is expected to double in the next five years, while the state's cattle population has reached its lowest point since 1951. Here's how these facts could combine to turn bourbon distilleries into a new source of biofuels.
-
We naturally pick up microorganisms as we move about the world. Now, researchers have developed an AI tool that accurately links you to a particular location using a sample of the bugs you’ve collected on your travels – like a bacterial satellite navigation system.
-
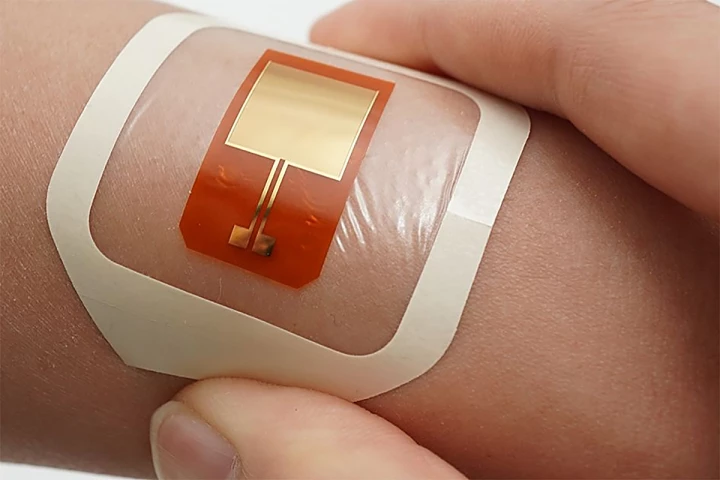
As more bacteria become increasingly resistant to antibiotics, we need more ways to fight infections. That's where this new patch comes in. With a gentle electric zap, this wearable could prevent bacteria from doing a number on us through our skin.
-
A. baumannii bacteria is a nasty antibiotic-resistant bug that thrives in hospitals, where it takes advantage of weakened immune systems. Researchers have now found the bacteria's secret weapon and have ideas on how to use it for good.
Load More