FDA
-
In a landmark shift in how mental health conditions are treated in the near future, the US Food and Drug Administration has approved the first at-home brain-stimulation device that can rapidly relieve moderate to severe depression symptoms.
-
Millions of Americans can now look forward to a better time traveling, with the US Food and Drug Administration approving a novel oral pill that helps prevent motion-induced vomiting – the first of its kind in more than 40 years.
-
The next transformative phase of weight-loss medication is upon us, with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approving Novo Nordisk's highly anticipated oral GLP-1 drug – with a starting dose available in early January for US$149.
-
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the first intranasal diuretic for heart, liver and kidney disease patients, aiming to prevent a common and costly issue that results in more than a million hospitalizations each year.
-
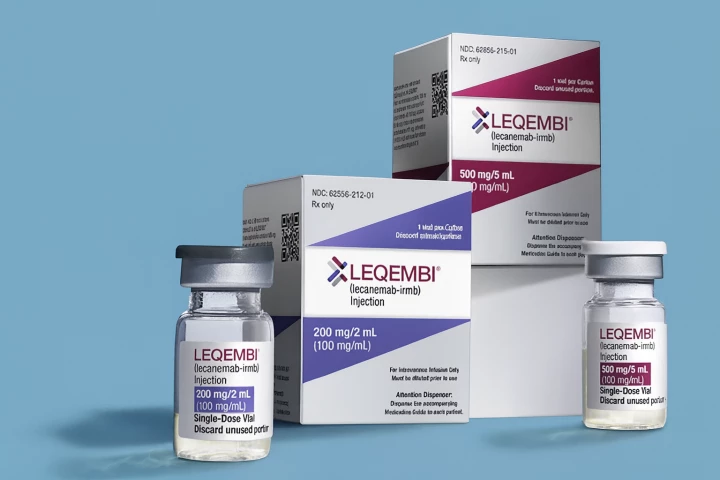
The FDA has approved a new version of an Alzheimer’s disease drug that can be given as a quick at-home weekly injection, offering patients a more convenient option than lengthy infusion-center visits. It will be widely available from October 6, 2025.
-
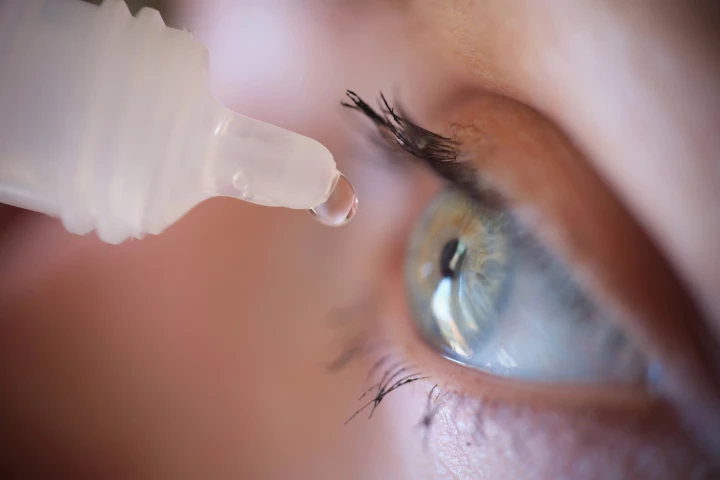
The first aceclidine-based eye drop to improve near vision in adults with age-related presbyopia, which affects more than 100 million adults in the US alone, has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and will be on sale by November.
-
The US Food and Drug Administration has instructed all GLP-1 drug-makers to update warning labels to include the risk of serious kidney injury that can result from dehydration. This comes after cases of acute kidney injury have required hemodialysis.
-
In a comprehensive new study looking at 39,763 different foods and drinks from the biggest 25 companies in the country, scientists discovered that almost 20% rely on synthetic food dyes to attract consumers. Now, the fight is on to ban them for good.
-
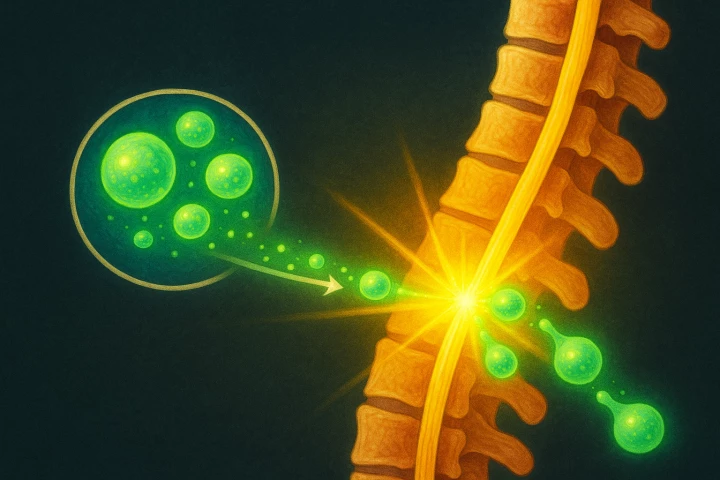
A paradigm shift in the way we treat spinal injuries is now in sight, with the world's first regenerative cell therapy approved for a Phase I clinical trial. It's a historical milestone that could reverse what has, until now, been an incurable injury.
-
A new antibiotic to relieve stubborn urinary tract infections and a blood-clot dissolving treatment for acute ischemic stroke will be commercially available in the coming months. It's been nearly three decades since adjacent drugs have hit the market.
-
Americans will soon have access to an infusion treatment that provides round-the-clock relief of Parkinson's symptoms. The US FDA has green-lit this innovative drug delivery system, which is expected to be available in the fourth quarter of 2025.
-
HIV has become a more manageable condition in recent years, but a full cure remains elusive. Now, scientists have found promise in permanently eliminating the virus, thanks to a drug already approved by the FDA to fight cancer.
Load More