Mayo Clinic
-
Heart attacks in younger adults aren’t always due to clogged arteries. A new major study reveals striking differences between men and women, with nontraditional causes playing a big role in women’s heart health.
-
Borrowing a cancer cell’s disguise, scientists shielded insulin-producing cells from attack by the immune system, a breakthrough that could pave the way for targeted type 1 diabetes treatments without whole-body immunosuppression.
-
Neighborhoods near golf courses are often considered desirable locations. However, a new study suggests that houses within a few miles of manicured fairways and greens may not be such hot property for your health and wellbeing.
-
A study has found that some gastrointestinal disorders are associated with an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. The research provides further evidence to support the hypothesis that the neurodegenerative disorder begins in the gut.
-
A group of US and Canadian anesthesiologists has sounded the alarm on the new class of weight-loss drugs, this time warning that they can increase the risk of serious complications for patients under sedation on the operating table.
-
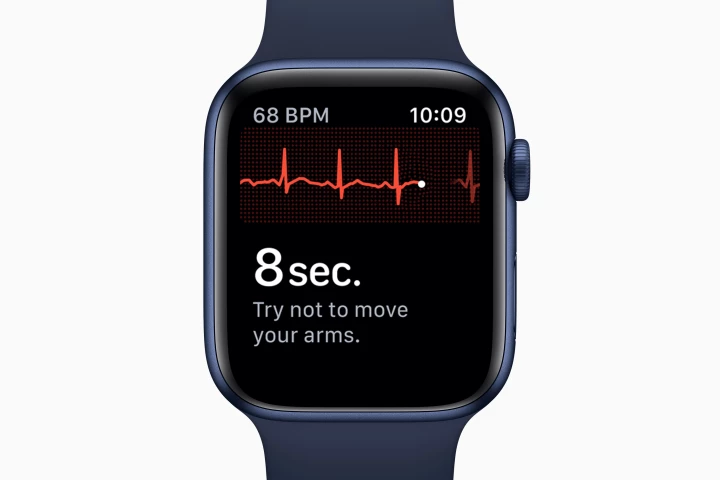
A new algorithm can effectively detect patients with a dangerous heart dysfunction using ECG data gathered by an Apple Watch. A large trial is now currently underway looking to test the clinical utility of the algorithm in one million people.
-
Through experiments on mice and humans, Mayo Clinic researchers have shown that an emerging class of drugs called senolytics can help protect against aging and its related diseases, by acting on a protein long associated with longevity.
-
A new peer-reviewed study is suggesting mRNA COVID-19 vaccines can prevent infection and reduce risk of onward transmission. The research is one of several real-world studies looking at the first few months of vaccinations.
-
Researchers at the Mayo Clinic have developed a test, called the Gut Microbiome Health Index, that can predict a person’s general health status by measuring the levels of 50 gut microbial species.
-
The US, like much of the world, is moving to keep contact between its residents to minimum as it grapples with the spread of coronavirus, and a new project taking place at the Mayo Clinic is exploring what this could mean for medical testing.
-
New research from the Mayo Clinic is raising doubts over the hypothesis that "lipid pneumonia" is responsible for the current vaping crisis.
-
Researchers from the Mayo Clinic have identified a new target in the battle against dementia and age-related cognitive decline – zombie cells. The study reveals that many pathological signs of neurodegenerative disease can be eliminated by removing these cells from the brain.
Load More