Nanoparticles
-
A new MIT method eliminates the need for hour-long infusions of antibodies for immunocompromised patients. With highly concentrated particles of antibodies created without a centrifuge, mass-manufacturing of better single-shot antibodies is here.
-
Researchers at MIT have just developed a new lipid nanoparticle that super-enhances the effectiveness of the mRNA vaccine in mice to a hundred times its stand-alone effectiveness, reducing required dosages while also reducing toxicity in the liver.
-
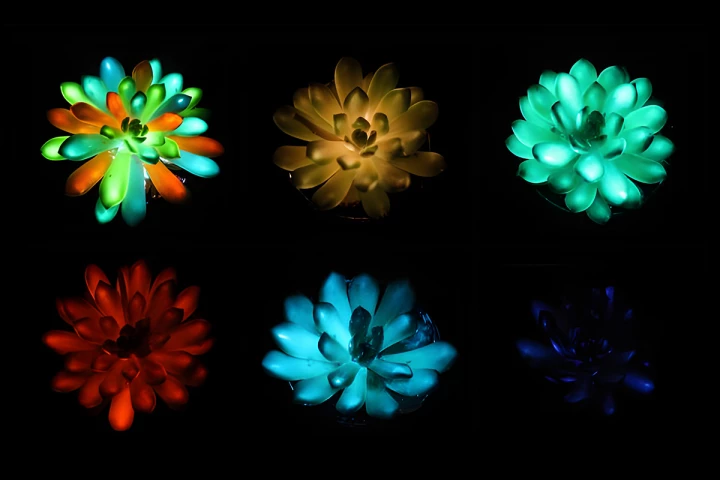
Wouldn't it be great if the plants in your home could do more than just sit there looking pretty? Researchers in China have found a way to upgrade succulents into soft glowing night lights in a range of hues, with the use of nanoparticles.
-
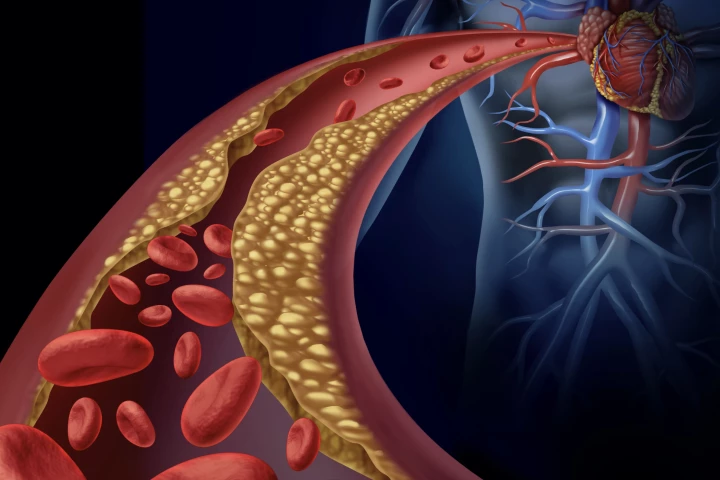
A new generation of nanoparticles can detect, shrink and clear plaques in the arteries, lowering inflammation and drawing out harmful cholesterol to be cycled via the liver. They offer a new way of diagnosing and fighting heart disease without drugs.
-
Hair care may be turning your bathroom into a hazardous emissions zone, as scientists find that 10-20 minutes of styling with common products and tools resulted in 10 billion ultrafine particles being inhaled and able to cross into the bloodstream.
-
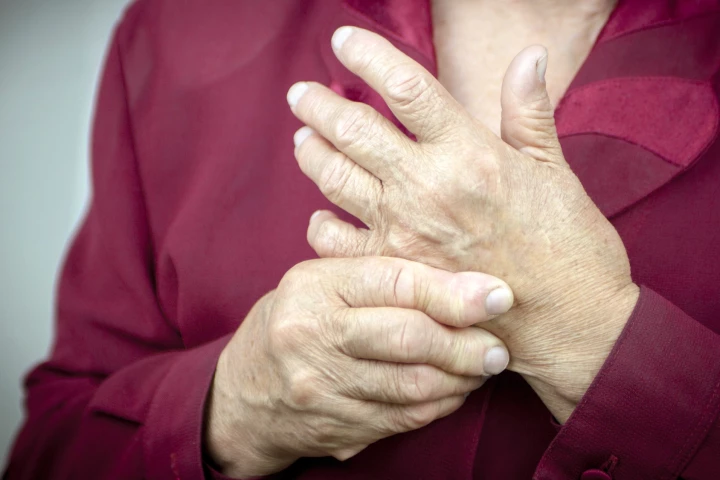
A new nanoparticle drug has shown preclinical promise in both preventing rheumatoid arthritis and reducing painful flare-ups, offering hope for a targeted, steroid-sparing treatment that calms the immune system without widespread suppression.
-
Japanese scientists have created what may be the world’s smallest video game. Using a regular controller, players can control a tiny digital ship, firing nanoscale bullets to push around a physical polystyrene ball just a few microns wide.
-
Using scented products indoors changes the chemistry of the air, producing as much air pollution as car exhaust does outside, according to a new study. Researchers say that breathing in these nanosized particles could have serious health implications.
-
There's a growing body of evidence that gold nanoparticles can trigger significant weight loss that targets fat, without affecting muscles, plus heal organs and improve blood-glucose levels. A new study makes a strong case for the first-ever human trial.
-
Whether a medication is taken orally or intravenously, it ends up traveling throughout the body instead of going solely to the place it's needed. Such could soon no longer be the case, however, thanks to a new microparticle that looks like a flower.
-
Using nanoparticles, researchers have created a sensor that selectively detects levels of cortisol, a well-known stress biomarker. Their cheap and easily reproducible device brings us a step closer to stress testing from the comfort of home.
-
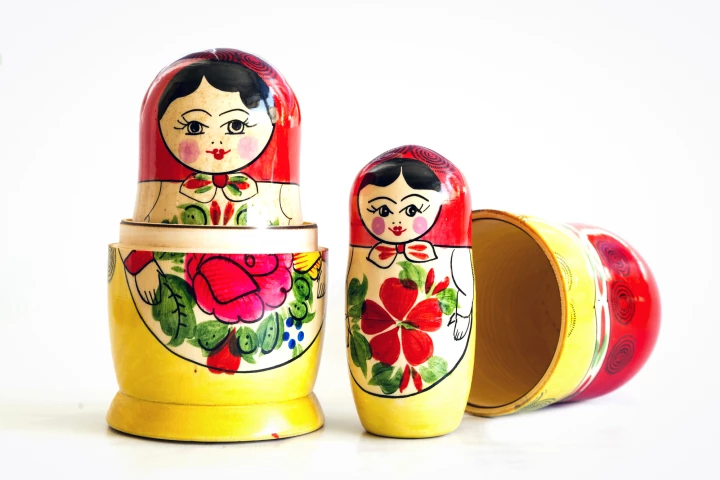
Researchers have developed technology that creates nanoscale sacs containing a compartment within a compartment, like a Russian matryoshka doll. The novel tech is capable of delivering two drugs simultaneously or at different times.
Load More