Rice University
-
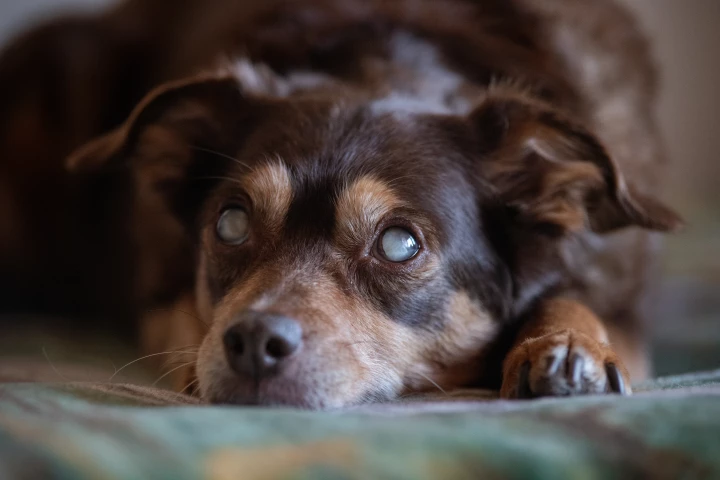
A team of researchers at Rice University has developed a haptic feedback vest and camera system for a blind dog known as Kunde. The vest helps guide the dog through daily obstacles and the hope is that it will soon do the same for other pups.
-
Brain-computer interfaces may allow paralyzed people to perform basic tasks, but there's more to life than eating and typing. That's where a new BCI comes in, as it has allowed a man to fly a virtual drone just by thinking of moving his fingers.
-
Lithium-ion batteries power everything from our vape pens to electric cars, but they have one glaring issue: they rely on lots of hard-to-harvest lithium. A new reactor from Rice University is set to make the whole process easier and safer.
-
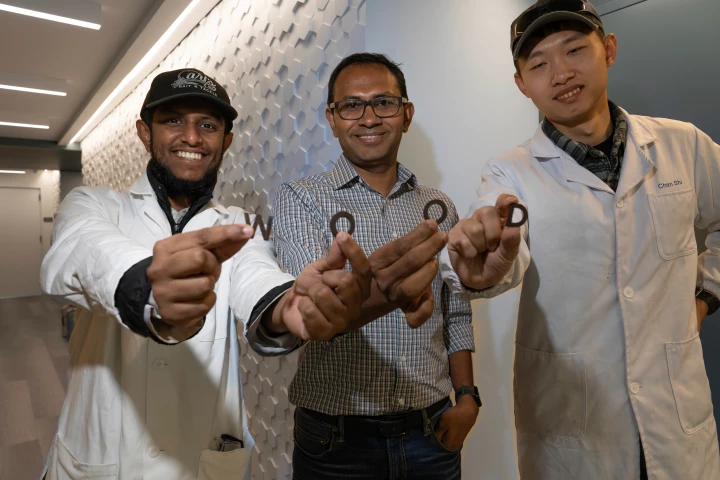
Lithium is a finite resource, and the more we lock inside rechargeable batteries, the less we have to use. A new speedy method to free the element from such sources could be a game changer in terms of the material's availability.
-
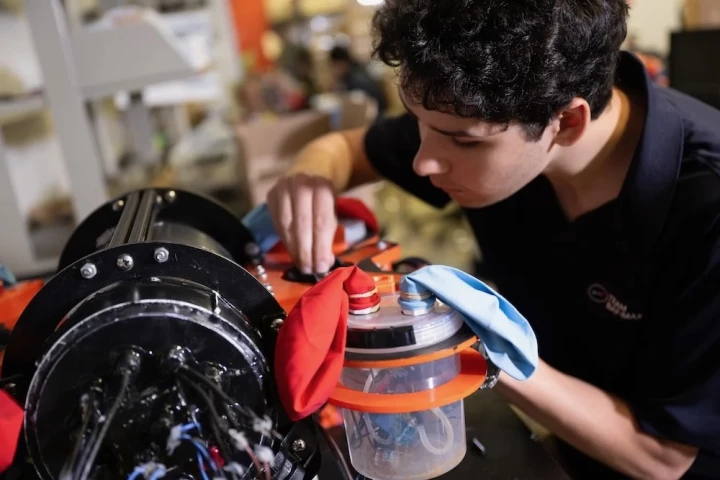
If scuba divers use inflatable BCDs (buoyancy control devices), why don't underwater robots? Well, an experimental new one does, and the technology is said to be much more energy-efficient than traditional methods of moving up and down in the water.
-
Scientists have developed a new "ink" that allows objects to be 3D-printed out of wood. The material could reduce the amount of wood that gets wasted in the manufacturing of various products, plus it could utilize existing wood waste.
-
Scientists have demonstrated an intriguing new technique to treat cancer – “molecular jackhammers” that latch onto cancer cells, then vibrate vigorously to kill them when activated by infrared light.
-
Thanks to our high demand for concrete, the world may eventually run out of accessible sand. Scientists at Rice University have now shown that substituting graphene can not only save sand, but makes concrete lighter, stronger and tougher.
-
Purifying polluted soil can be a difficult process, often requiring the soil to be dug up and transported to an offsite remediation facility. Now, however, scientists have developed an eco-friendly method of treating it where it lays – by zapping it.
-
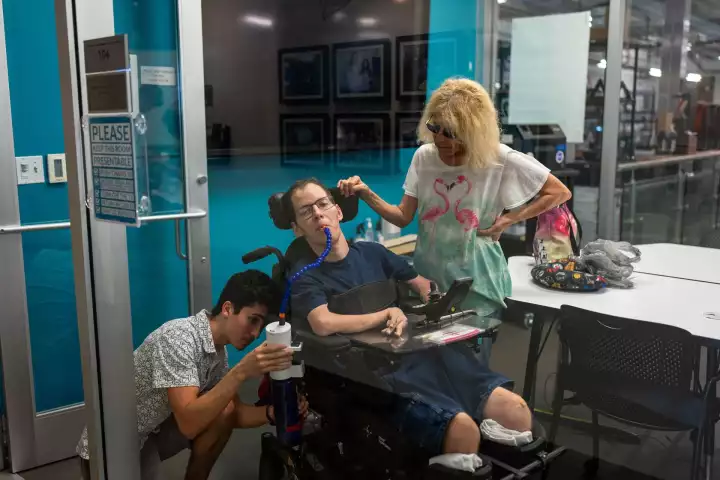
For people such as Gary Lynn, cerebral palsy makes it nearly impossible to perform tasks like getting a sip of water without human assistance. He can now get those sips on his own, however, thanks to a student-designed device known as the RoboCup.
-
In a move that echoes a sci-fi series, researchers have developed a material that was able to not only stimulate nerves in rodents, but reconnect them as well. The finding could lead to injectable particles that take the place of larger implants.
-
Splitting the gene editor used in traditional CRISPR technology creates a more precise tool with significantly less chance of causing unintended mutations, a new study has found. The novel tool could correct half of the mutations that cause disease.
Load More