University of Massachusetts
-
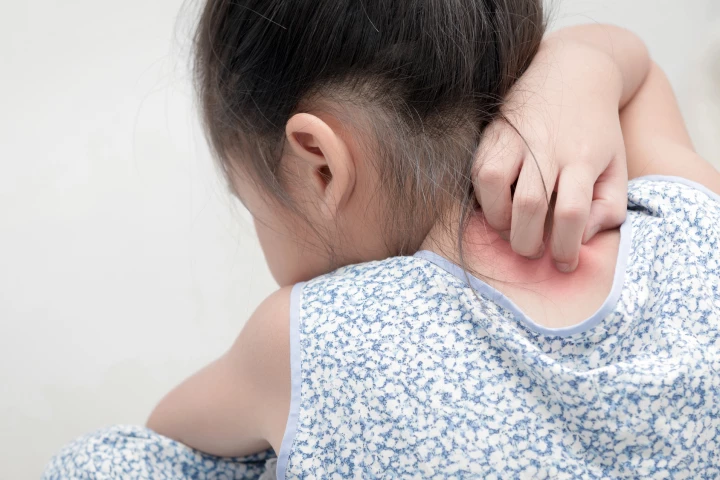
Children exposed to the common antimicrobial triclosan were more likely to develop allergic symptoms, a new study has found. It raises fresh concerns over the health impacts of a chemical widely used in everyday products.
-
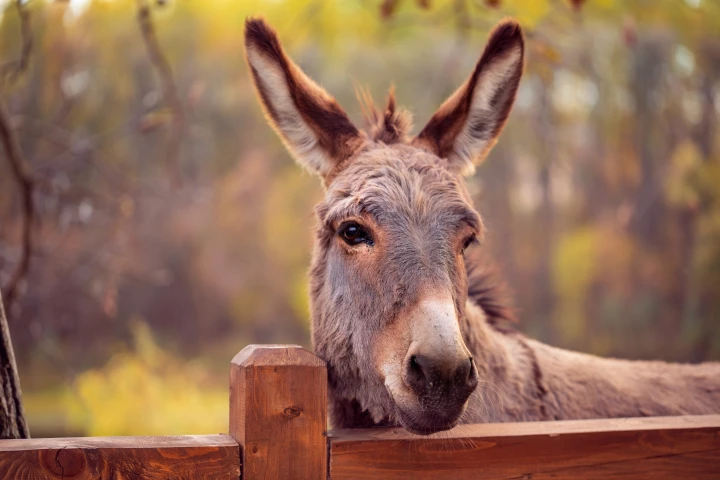
It turns out that donkeys are exceptionally good at repelling deer ticks. Now, researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have harnessed that ability to create a natural bug repellent that proved as effective as DEET at fighting the pests.
-
If your home has old lead water pipes, there's a chance that harmful concentrations of lead may be present in your water. An experimental new device could soon allow homeowners to check for themselves, instead of waiting for the city to do so.
-
A “bananageddon” might be on the horizon, and not for the first time. But new research could help save our favorite fruit.
-
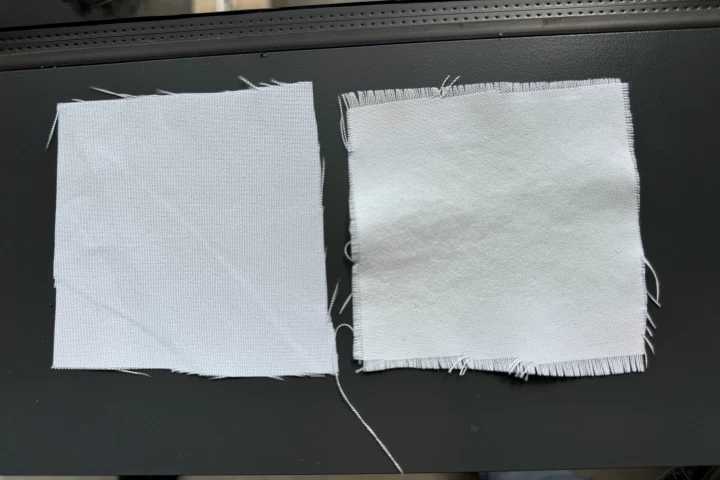
When it comes to keeping cool on hot days, it's not so much a matter of wearing less clothing as it is a matter of wearing the right clothing. A new fabric coating could help in that regard, and it's essentially made of chalk.
-
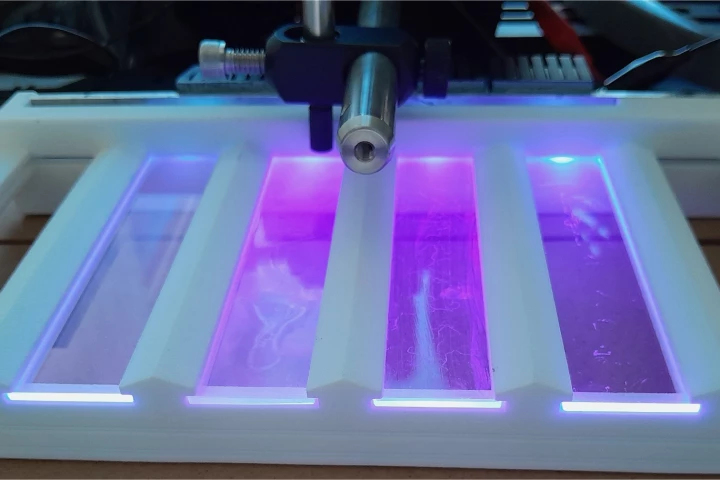
Scientists are using UV-emitting glass to keep problematic undersea biofilms at bay. The technology may find use in applications such as underwater viewing ports and camera lenses, and perhaps even one day the hulls of ships.
-
Researchers are developing a robotic exoskeleton platform that could overcome the limitations of treadmills used during the rehabilitation of the many stroke survivors who have problems walking.
-
A new study has linked preconception exposure to phthalates to reduced odds of getting pregnant, adding to a growing body of evidence about the negative effects of these chemicals, commonly found in personal care products like soap and shampoo.
-
Cancer vaccines are a medical holy grail – but what if you could repurpose a vaccine you’ve already had? Scientists have demonstrated in mice a way to trick the immune system into attacking tumors by mistaking them for a pathogen it already targets.
-
When doctors want to see if someone has a certain illness, they may check the patient's blood or urine for the DNA of a specific virus or bacteria, or for a mutated version of the person's own DNA. A new device should make doing so much easier.
-
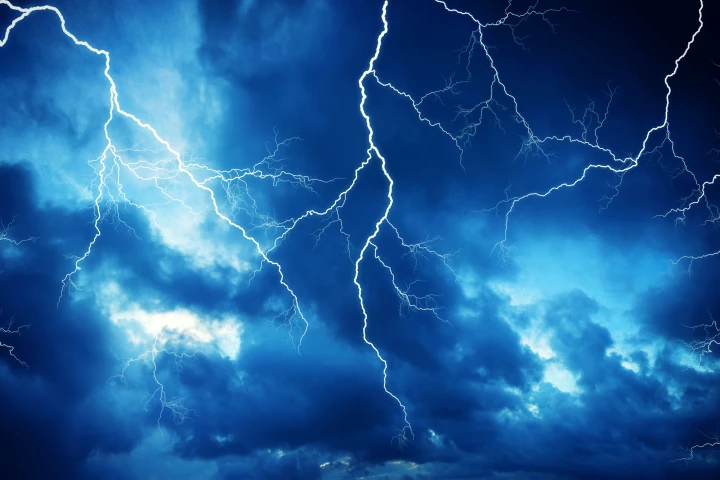
As anyone who's ever seen a bolt of lightning knows, the air around us can be filled with an astonishing amount of energy. A new study shows a way to harvest this power using a perforated nanofilm that can be made from a vast variety of materials.
-
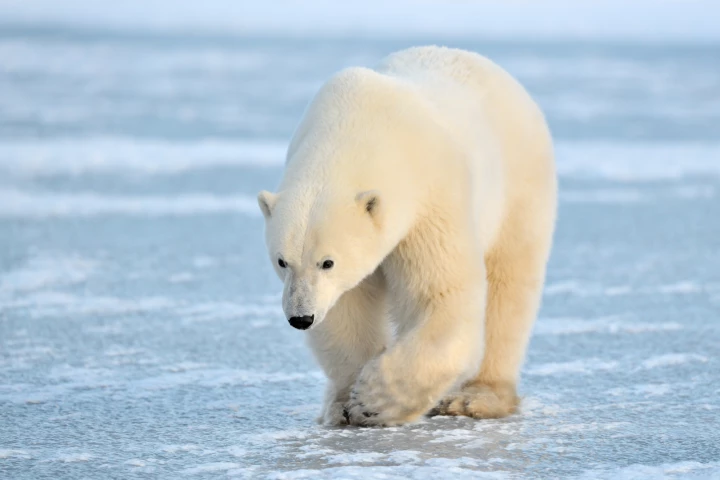
To develop a heat-trapping fabric, researchers looked to polar bears, who thrive in incredibly low temperatures. The secret, they found, has to do with a relationship between the bears' hollow translucent hair and the black skin that lies beneath.
Load More