Virginia Tech
-
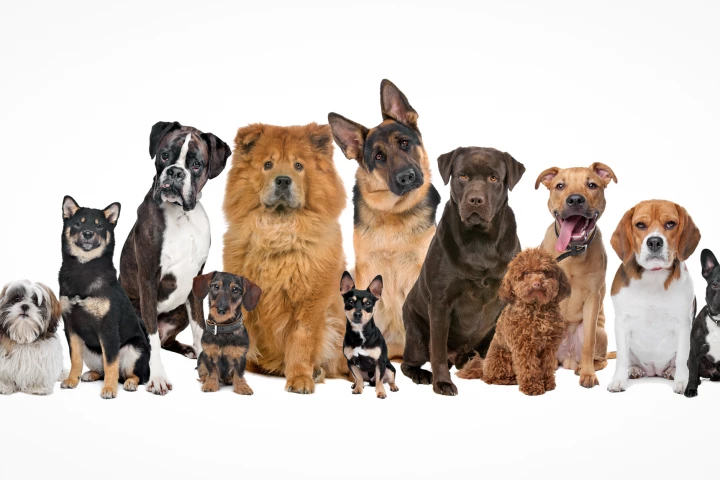
The largest-ever study of dog behavior, tracking more than 47,000 pets, reveals how breed, size, sex, and age shape canine traits. It provides insights that could help identify early signs of illness and improve training and welfare.
-
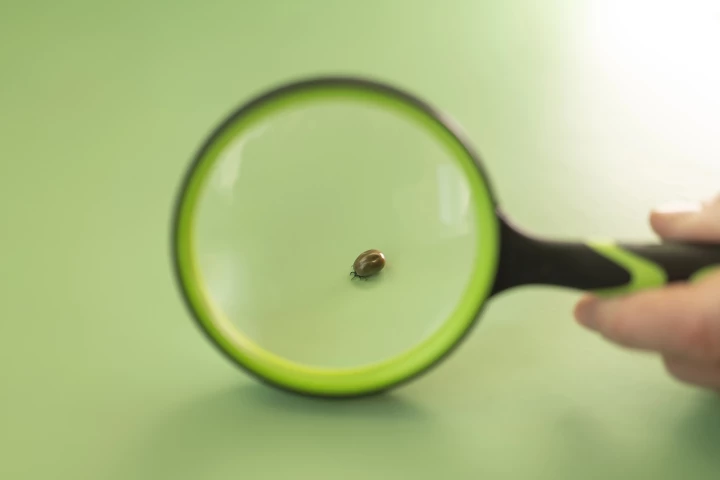
From fleas to mosquitoes, there's no shortage of organisms we consider pests. But thanks to new genetic detective work, scientists have named and shamed the resilient, highly adaptive – and frustratingly hard to kill – bug that got to us first.
-
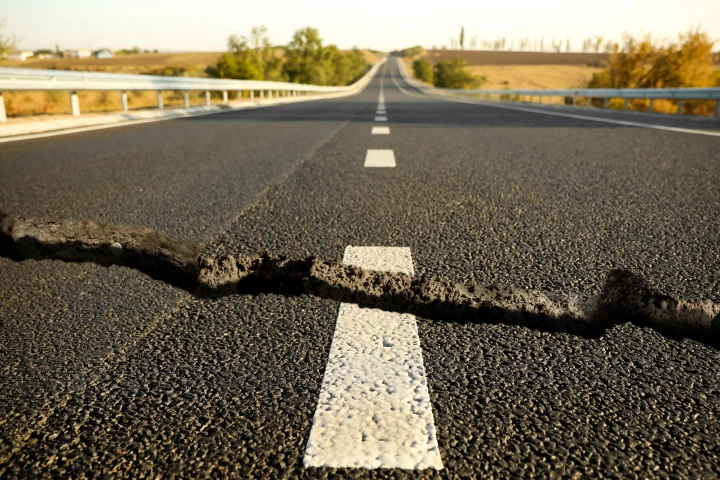
An alarming new report reveals that right across the country, 28 US cities are sinking, showing the kind of geologic subsidence that could impact buildings and infrastructure sooner rather than later. But, scientists say it's not yet too late to fix.
-
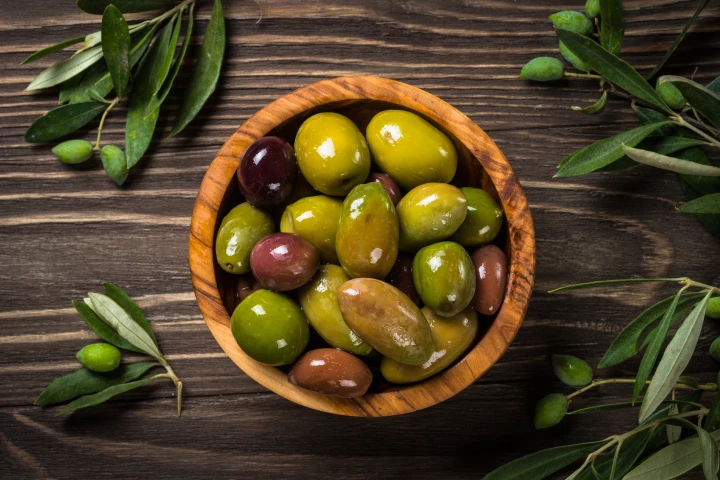
A compound that occurs in mature olives and olive oil can regulate glucose and ramp up weight loss in rapid time, mimicking the effects of existing medication. This opens the door for developing safe, natural treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
-
Inflammation from a viral infection has traditionally been thought to cause acute myocarditis, which can lead to fatal heart arrhythmias in healthy young adults. Now, it seems it's something else that damages heart cells before inflammation kicks in.
-
Ordinarily, adhesive tape either boasts a strong hold or is easy to remove. Drawing inspiration from an ancient paper-cutting technique, however, scientists have now devised a method of combining both qualities in existing types of tape.
-
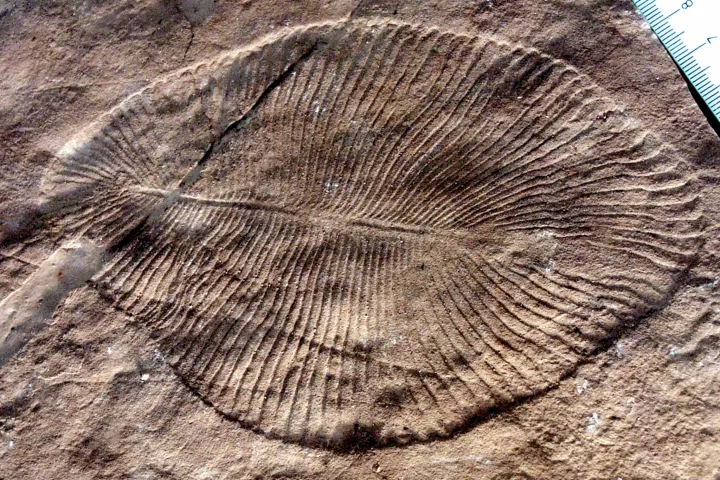
It's thought the Earth is currently entering its sixth major extinction event, but a new study suggests it may actually be the seventh. Scientists have found evidence of a previously unknown mass extinction event that struck half a billion years ago.
-
Polystyrene is a problematic material when it comes to recycling, but a team of Virginia Tech researchers is hoping to change this with a novel method that turns it into a product of relatively high value.
-
Scientists have developed a glove for gripping underwater objects that takes its design cues from an octopus, featuring rubber suckers and a sophisticated sensing capability that mimic the sea creature's unique muscular and nervous systems.
-
Most robots are designed for a specific job, and aren’t very adaptable. But a new soft robot can morph into a range of shapes for driving, flying or swimming, thanks to a rubber skin full of a metal that switches between liquid and solid forms.
-
Not only are surgical scars unsightly, but their limited elasticity can also reduce the patient's range of motion. There may be new hope, though, as a recent study has shed light on how a therapeutic peptide could drastically reduce such scarring.
-
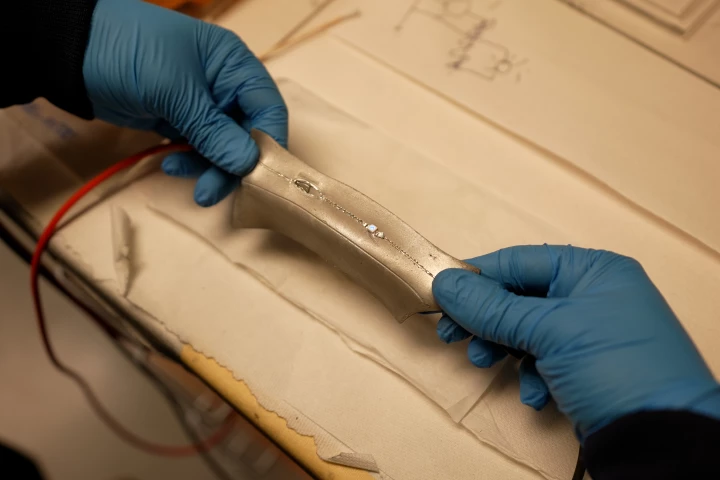
Soft robots and flexible electronics aren't as protected as their rigid-shelled counterparts, so they're more likely to get ripped or punctured. A new stretchable, self-healing conductive material was designed with this limitation in mind.
Load More