Children
-
A new study has revealed that kids who face exclusionary discipline at school were at greater risk of developing anxiety and depression. The research highlights the need to rethink how young students who act out are treated by educators.
-
While they might sound like healthy choices, a large study in Finland has revealed the detrimental impact of eating most fruits and several grains on diabetes risk. The study also revealed a helpful food ally in fighting off the disease.
-
Australia, the ‘allergy capital of the world,’ has launched a world-first free nationwide treatment program for children with peanut allergies. The goal is to safely build tolerance so that kids don’t need to worry about the possibility of a life-threatening reaction.
-
Canadian ebike maker Rocky Mountain has launch an adventure model called the Reaper Powerplay that's described as a "full-sized electric trail bike in a junior-sized package" and rides as the first mid-motor, full-suspension eMTB for kids.
-
Calls to US poison centers reporting intentional exposure resulting in deaths and serious harm to adults and children have risen significantly over a 15-year period, a new study found. Researchers say the alarming statistics warrant an examination of their root cause.
-
A new study led by researchers in Germany has for the first time compared the chemical composition of body odor between teenagers and infants, homing in on the exact compounds that make babies smell like flowers and teens smell like sweaty goats.
-
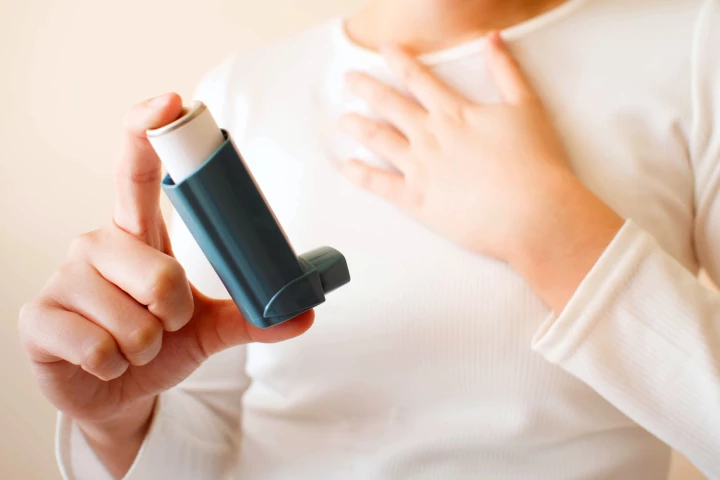
Combining census data with cutting-edge statistical analysis and satellite imagery, researchers have revealed a stark difference between inner- and outer-city living in terms of the risk children have of developing asthma.
-
Exposure to phthalates, a commonly used chemical in plastics, has been estimated to be the primary cause of one in 10 preterm births, according to a new study led by researchers from the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
-
New research has proved for the first time that RSV infection, common in young children, can penetrate nerve cells and may lead to nerve damage. The findings underscore the possible long-term effects of RSV and the importance of preventive measures.
-
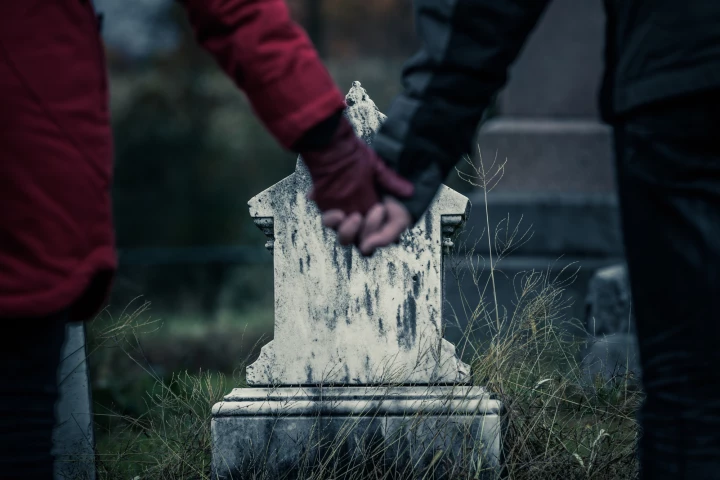
Research has linked the death of a sibling early in life to a 17% increased risk of cardiovascular disease, with most being early-onset. The findings highlight the need to provide support to bereaved siblings to reduce the risk of future health issues.
-
A study has found that using a digital support algorithm to guide treatment by healthcare providers significantly reduced the number of antibiotic prescriptions given to acutely sick children, without affecting treatment success or causing harm.
-
Researchers have used AI to screen photographs of children’s retinas to diagnose autism with 100% accuracy. The findings suggest AI is a viable screening tool for early diagnosis, especially when access to a specialist child psychiatrist is limited.
Load More