Heating
-
In a new study from the University of Oregon, scientists turned up the temperature to see which type of passive heat therapy packs the most health punch – hot baths, traditional saunas, or those fancy far-infrared saunas.
-
Nobody likes buildings that are too hot in the summer or too cold in the winter. That's where the FlectoLine facade comes in, as it uses two bio-inspired mechanisms to regulate how much solar thermal energy gets through a building's windows.
-
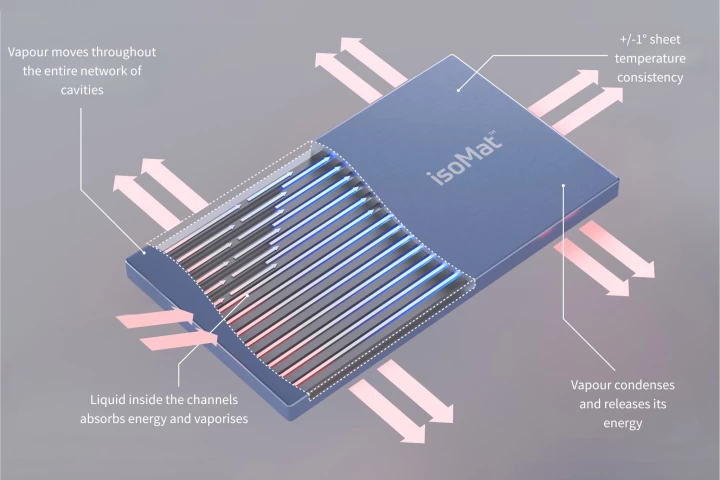
How's this for a set of promises? Flint Engineering claims its new, flat, thermal-transfer "IsoMat" can power entire homes, cut refrigerator energy consumption by 30%, and radically speed up EV charging while also extending battery life.
-
Imagine having a picture on your wall that completely changes when the room gets too warm. Engineers at MIT have created a new printing technology called Thermochromorph to make full-color images that switch in response to temperature.
-
Although sunscreen does help protect our skin from the sun's harmful UV rays, it isn't designed to keep that skin cool. An experimental new sunscreen does that very thing, however, while maintaining an SPF rating of about 50.
-
Cranking up the air conditioner keeps buildings cool, but it guzzles energy. Passive materials can regulate temperatures more efficiently, and now scientists have developed a new coating that keeps glass much cooler, while still being transparent.
-
If you find that you can never get the temperature quite right in bed, a new gizmo called the Homiffi could help. It cranks out either cool or warm air and also acts as a clock, a wireless charger, a Bluetooth speaker and more.
-
Scientists in Japan have developed a new organic device that can harvest energy from heat. Unlike other thermoelectric generators, this one works at room temperature without a heat gradient.
-
Supercritical geothermal power holds the promise of meeting humanity's energy needs for millions of years, but how practical is it? A new analysis by Karthik Subramanian of Lux Research suggests that it may lie somewhere between improbable and impossible.
-
Water can hold a huge amount of thermal energy, and a new system to tap into this is being trialed in Scotland. A startup called SeaWarm uses heat stored in bodies of water for buildings, pulling four times more heat out than electricity used.
-
A new heat-to-energy converter has reached a record efficiency of 44% – the average steam turbine manages about 35%, for comparison. This thermophotovoltaic cell is a major step on the way to sustainable, grid-scale renewable energy storage.
-
Extreme night-time temperatures significantly increase the risk of stroke, according to a new study. The researchers behind the study say that armed with these findings, people can better safeguard themselves against increasingly hot nights.
Load More