Nerves
-
The first-of-a-kind brain-stimulation device approved to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the US has had its efficacy questioned, with scientists believing that its Food and Drug Administration approval was based on poor science.
-
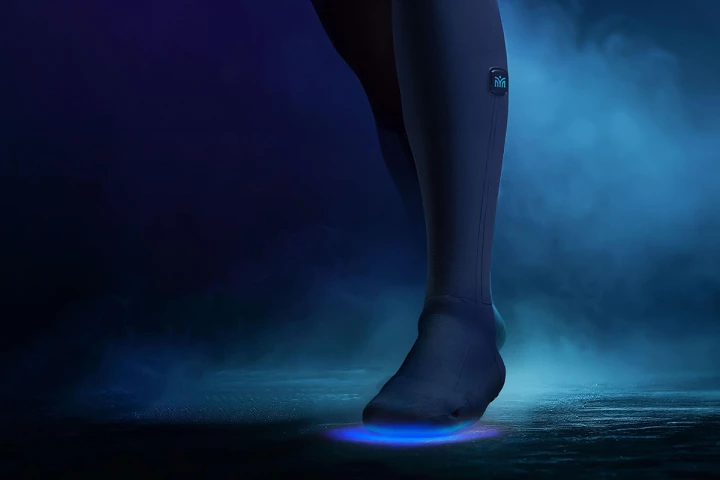
Researchers in Switzerland have stuffed a bunch of chips and sensors into socks to help people who suffer from some of the worst symptoms of diabetes – chronic pain and a loss of sensation in the feet that make it hard to walk.
-
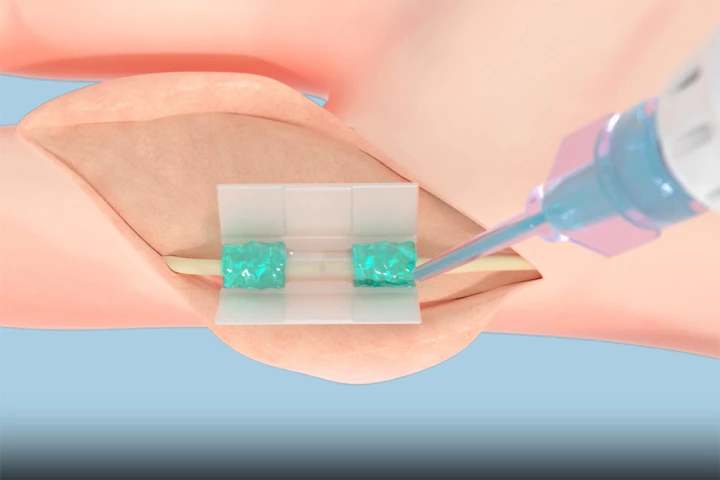
A new biocompatible polymer that helps glue and repair tissue without causing damage – initially developed at MIT – might be a better way to heal wounds than sutures and staples. When activated using blue light, it can securely attach to wet tissue.
-
In the ongoing search to find an intervention that does away with opioids, a new game-based system has shown huge promise in tackling chronic neuropathic pain. Using a game and a headset, it "trains" patients to rewire brain signals to relieve pain.
-
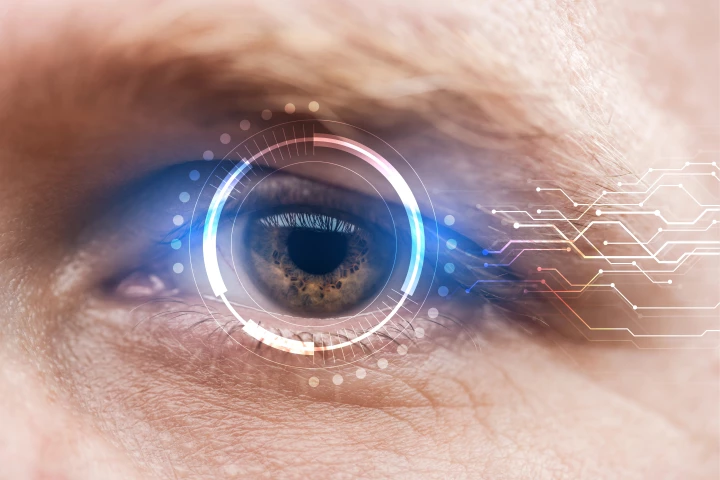
Pupil dilation and subtle facial changes in response to sound can reveal how severe tinnitus is. Through this, researchers have discovered a new way to objectively gauge how bad the condition is, more accurately diagnosing tinnitus and treating it.
-
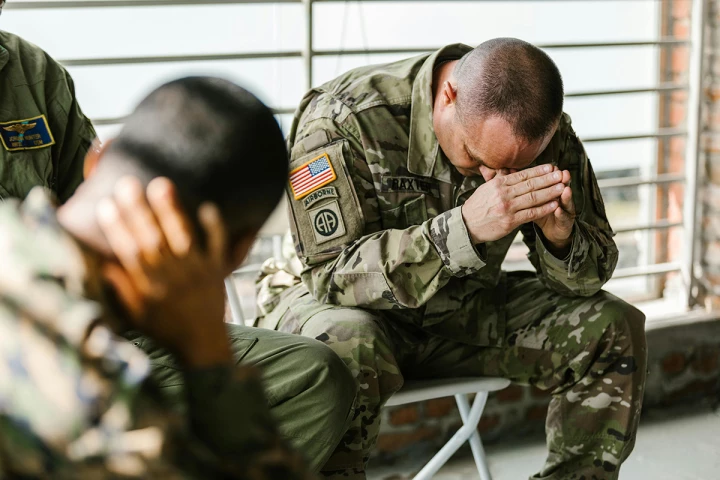
A group of Texas-based researchers has developed an effective way to treat post-traumatic stress disorder that involves zapping the vagus nerve around the neck, using a device the size of a shirt button.
-
Nerve or neuropathic pain has long been a tricky condition to treat effectively. However, a new study has comprehensively evaluated current drug and non-drug therapies to provide up-to-date guidelines to inform treatment options.
-
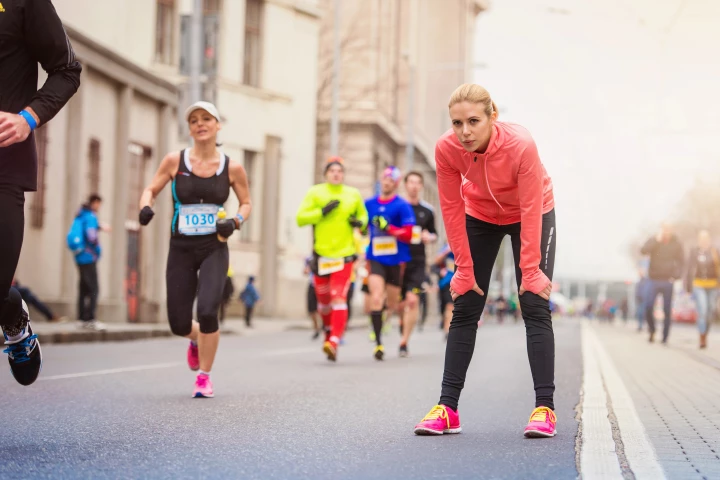
More than a million people of nearly all ages lace up their trainers and hit the pavement in a marathon every year. And while running has a suite of health benefits, a long-distance race may not be such good news for the brain in the weeks that follow.
-
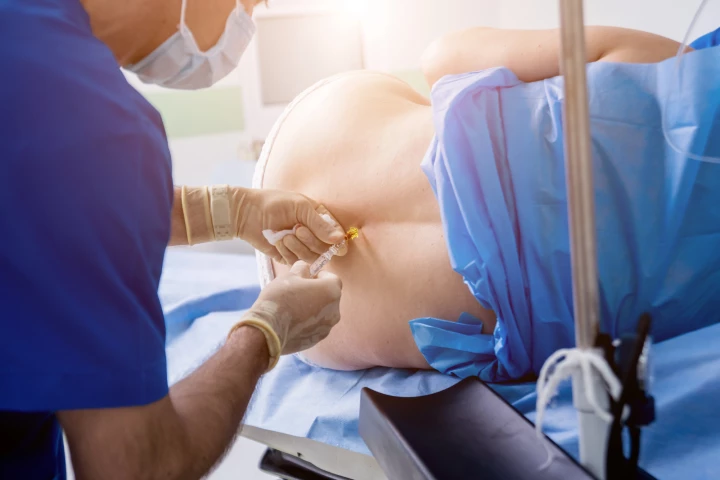
If you're thinking of getting an injection for back pain, you might want to think again. A panel of experts has examined the practice, found serious issues with its use – including financial gain – and issued strong recommendations to avoid it.
-
A pioneering once-a-day pill that regenerates nerve cell connections damaged by ALS has been FDA-approved for ongoing clinical trials. The drug is now being given to those with ALS and could be a watershed moment in the treatment of the fatal disease.
-
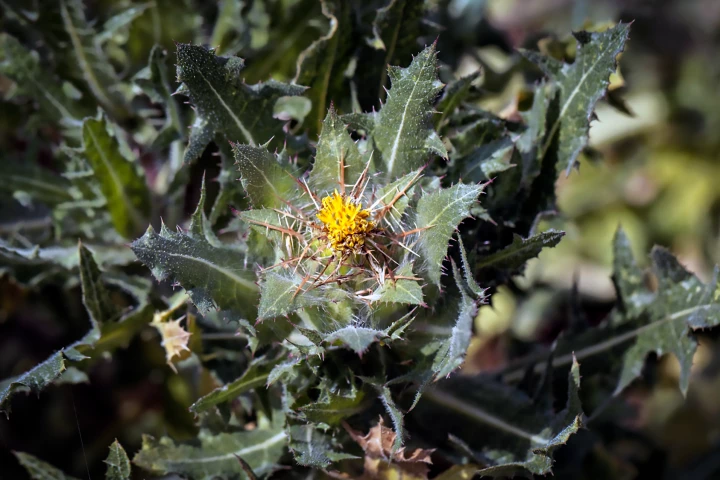
Nature has again proven effective in treating health conditions, this time nerve injury. According to a new study, a compound found in the blessed thistle plant accelerates the regeneration of damaged nerves, restoring motor function and touch sensation.
-
Researchers discovered a non-opioid compound that effectively reduced hypersensitivity associated with nerve pain caused by diabetes or chemotherapy drugs, opening the door to a drug to treat the condition for which existing painkillers do little.
Load More