RMIT
-
If you've ever had a packing peanut stick to your clothes as you unbox your Amazon delivery, then you know that Styrofoam is pretty good at generating static electricity. A new invention turns that quality into a workable energy-saving solution.
-
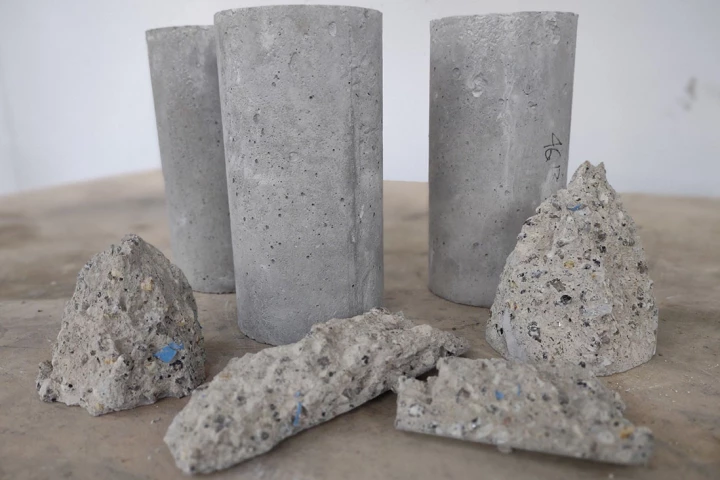
RMIT researchers have developed a new type of "green concrete" that incorporates twice as much recycled coal ash as existing low-carbon concretes, halves the amount of cement required, and lasts even longer than regular Portland cement concrete.
-
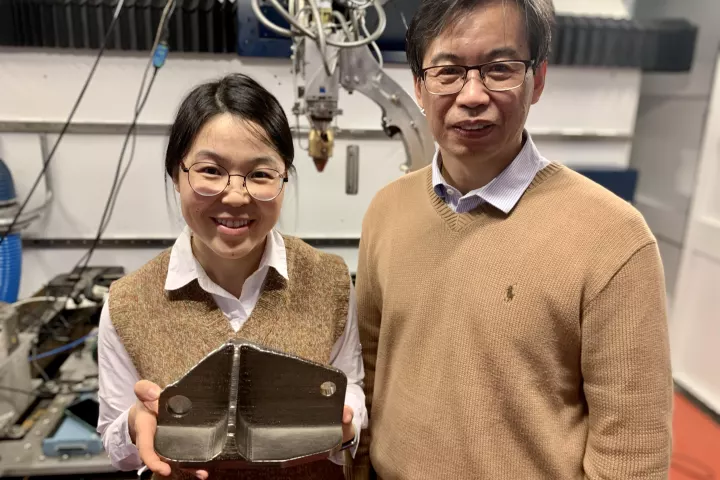
A new type of 3D-printed lattice structure has surprised researchers with its strength and light weight. It uses two different lattice structures merged together to eliminate the weak points normally found in these complex shapes.
-
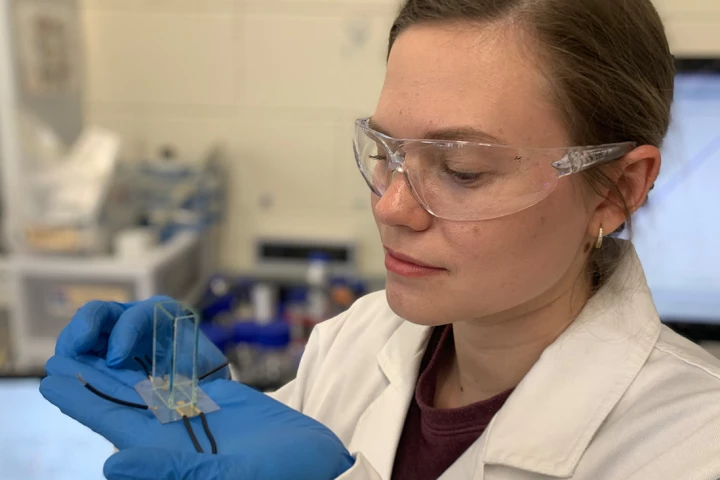
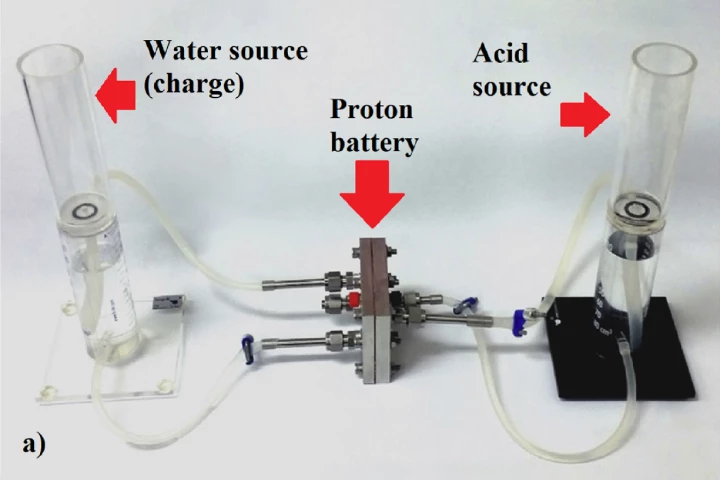
RMIT engineers say they've tripled the energy density of cheap, rechargeable, recyclable proton flow batteries, which can now challenge commercially available lithium-ion batteries for capacity with a specific energy density of 245 Wh/kg.
-
The communications and nutrients support system of fungi, mycelium, can stretch hundreds of miles beneath our feet. Now, researchers have harnessed another of its bio-superpowers to engineer a sustainable, safe and effective fire-retardant material.
-
A novel 3D-printing process has opened up a new class of strong, ductile, tuneable titanium alloys that could potentially be made from waste products, without expensive additives like vanadium. It may also work for zirconium, niobium and molybdenum.
-
Green hydrogen can't be viewed as environmentally friendly if it drinks huge amounts of fresh water, or results in the bulk output of toxic chlorine, according to RMIT researchers who say they've come up with a cheap technique that does neither.
-
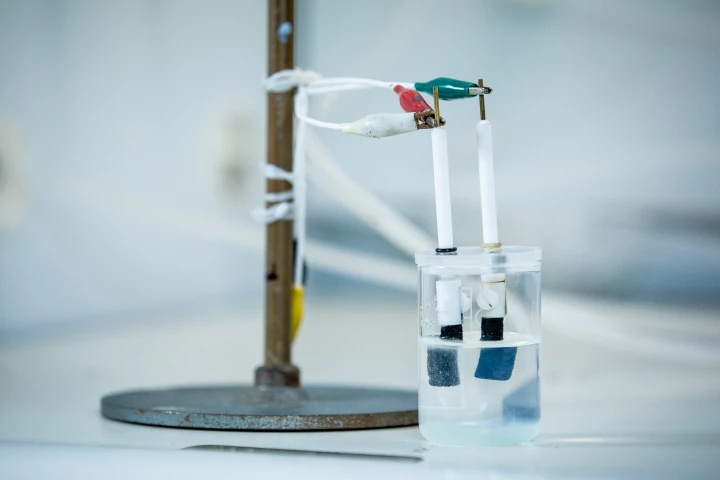
RMIT researchers say they've unlocked cheaper, more energy-efficient green hydrogen production with a new electrolysis technique boosted by sound waves. With these high-frequency vibrations active, standard electrolysis produces 14x more hydrogen.
-
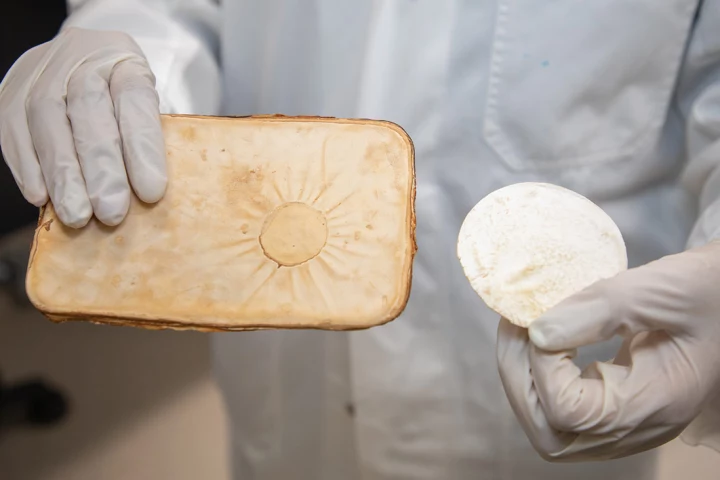
RMIT researchers claim FiberX can add up to 20% more healthy dietary fiber to food, without any detectable change to its color, texture or taste. Best of all, the team says it can be made from starches that would otherwise be agricultural waste.
-
Australian scientists have discovered strangely folded diamonds in rare meteorite samples. In investigating how they came to form, the team found evidence that they were forged in a cataclysm on an ancient dwarf planet.
-
RMIT scientists are looking to help tackle the mounting waste generated by the ongoing pandemic, by demonstrating a form of concrete that incorporates shredded personal protective equipment (PPE) for improved performance.
-
Getting an organ from donor to recipient is a race against time, with many going to waste. Now, researchers in Australia have identified new cryoprotectants that could preserve organs and tissues for much longer without damaging them.
Load More