T-cells
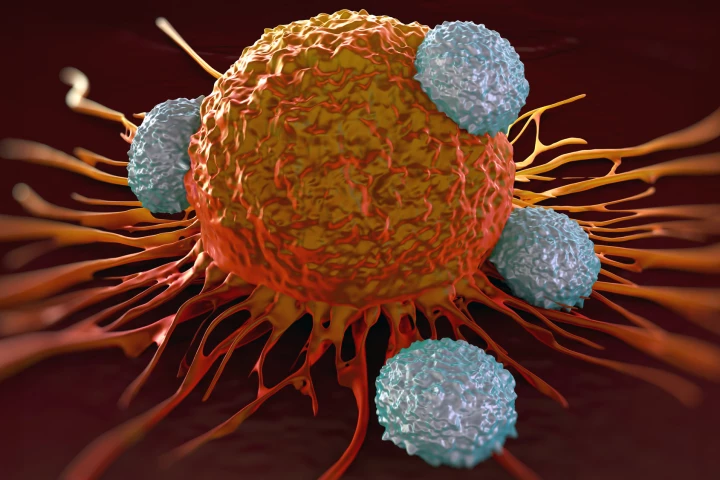
T cells are a type of white blood cell that plays a central role in the immune system by identifying and attacking infected or abnormal cells.
-
Researchers have demonstrated how a secret weapon made in the gut, produced by consuming pomegranate and walnuts, can rejuvenate the immune system in middle age, shielding us from cell damage, inflammation and chronic diseases including cancer.
-
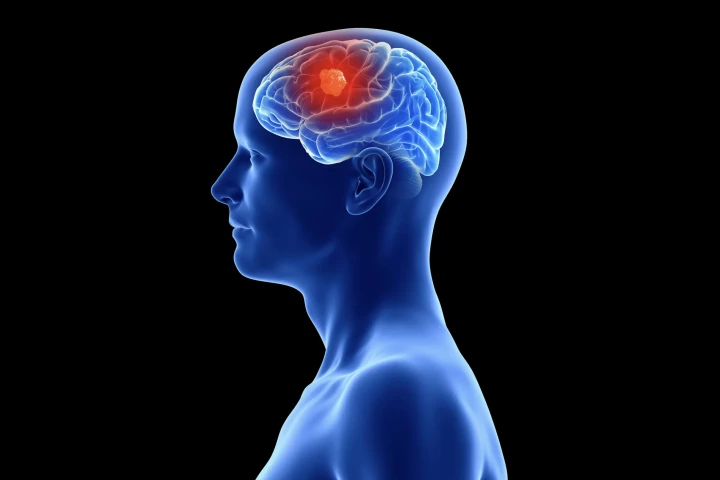
For the first time, scientists have detailed how glioblastoma has a unique path of progression, aggressively gnawing away at the skull bone itself to affect marrow – explaining why drugs that are intended to impede its growth end up making it worse.
-
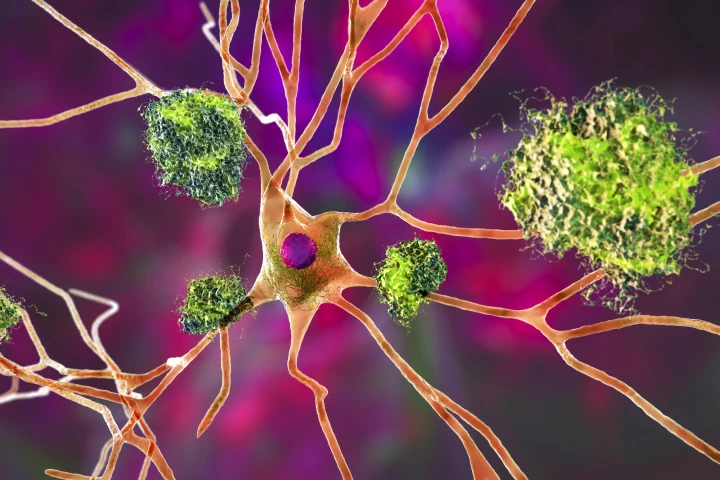
A protein notorious for its role in Alzheimer’s disease may hold the key to supercharging the aging immune system. Scientists showed that a byproduct of amyloid-beta rejuvenates T cells, boosting their tumor-fighting power and slashing cancer risk.
-
New research shows lymph nodes aren’t just cancer bystanders, they’re the command centers fueling immune attacks. Surgically removing them along with tumors may weaken treatment, while preserving them could supercharge it.
-
Signs of immune system aging appear years before rheumatoid arthritis takes hold, offering new hope for early diagnosis and treatments that could slow or stop the disease before it starts, according to new research.
-
A carotenoid widely available in fruit and vegetables, and as a supplement, has been found to bolster the cancer-killing capacity of immune cells. It could be a valuable ally in immunotherapy treatment, helping to shrink tumors more effectively.
-
Scientists have created a hydrogel “rest stop” that shields cancer-fighting T cells, delaying their exhaustion and boosting their killing power. The game-changing strategy could supercharge immunotherapy, giving T cells time to regroup and hit harder.
-
New research found that drinking camel milk can reduce the severity of asthma caused by house dust mites, a major trigger. While the research is still in the early stages, it opens the door to using camel milk in combination with existing therapies.
-
Researchers have uncovered another piece of the Parkinson’s disease puzzle, identifying that particular immune cells are active long before the hallmark motor symptoms become apparent. It paves the way for the development of earlier diagnostic tools.
-
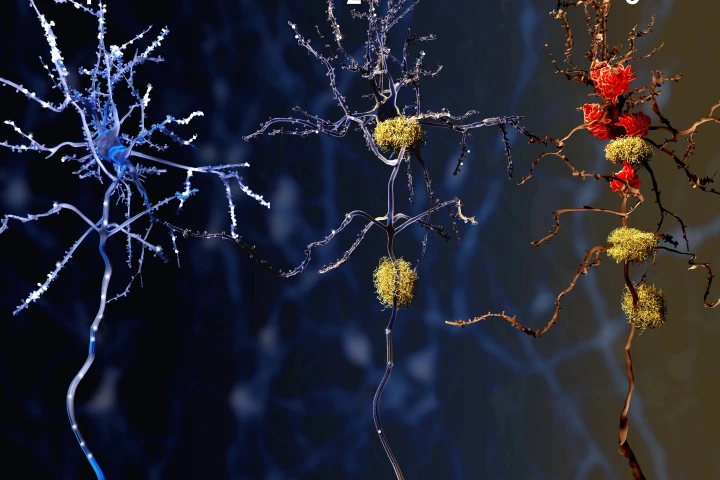
Taking inspiration from the CAR T-cell technology used to provide personalized cancer treatments, researchers have conducted a proof-of-concept study showing how similar compounds can precisely target protein tangles and plaques in the brain.
-
In a breakthrough finding, researchers have discovered that immune cells near the spinal cord are triggered by estrogen and progesterone to produce a natural painkiller called enkephalin. The finding could change the way we treat chronic pain.