University of Alberta
-
A landmark study has found that a workable exercise plan significantly improves survival and health of people who have survived colorectal cancer. So much so that, as one researcher notes, "Our findings will change the way we treat colon cancer."
-
Left untreated, frostbite can lead to the amputation of fingers and toes. That's where a new Canadian system comes in, which will allow frostbite to be treated quickly, effectively and on location … utilizing culinary-inspired technology.
-
The discovery of a quartet of fossilized snakes, a never-before-seen species of boa that lived 38 million years ago, has provided scientists with a rare insight into reptilian social behavior and provided clues about the evolution of its modern ancestors.
-
While we don't like to talk ill of the dead, new analysis has called into question the intelligence of the king of the dinosaurs. It upends last year's findings that likened the cognitive skills of the Tyrannosaurus rex to that of a primate.
-
The Andean condor’s drag-reducing aerodynamic wings have inspired the creation of a winglet, which, when added to a wind turbine blade, boosted energy production by an average of 10%, according to a new study.
-
Researchers developed a technique to implant a device containing insulin-secreting cells in a pocket under the skin, reversing diabetes in mice without the need for anti-rejection drugs. It could one day provide an alternative to insulin injections.
-
A new study has found that combining radiotherapy with a cancer-targeting virus was more effective at combatting a hard-to-treat, deadly form of brain tumor than using either therapy alone. The finding may lead to more effective cancer treatments.
-
Researchers have discovered an old class of antipsychotic drugs may offer clues to a novel kind of treatment for type 2 diabetes. While the drugs may be directly repurposed, they could also be slightly modified to specifically target blood sugar control.
-
It has long been known that some of the earliest mammals coexisted with the later-period dinosaurs. Now, for just the second time ever, scientists have documented fossil evidence of a dinosaur having actually eaten one of those mammals.
-
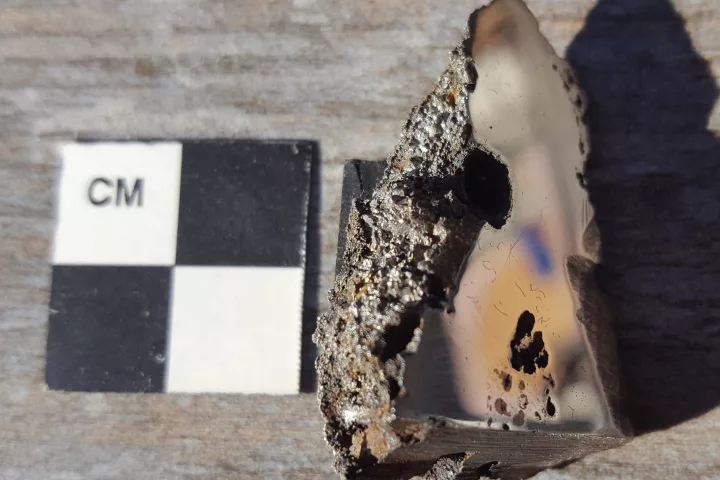
Scientists have discovered at least two new minerals inside one of the largest meteorites ever found. The iron-based minerals have never been spotted in nature, and could hint at unknown geological processes and new material uses.
-
A trial testing fecal transplants in obese subjects with metabolic syndrome found the treatment was only beneficial when accompanied by non-fermentable fiber supplements. The trial saw improvements in insulin sensitivity 6 weeks after a fecal transplant.
-
The University of Alberta has developed a new technique for 3D printing cartilage in custom shapes. This can be used to repair the noses of skin cancer patients, saving them the trouble of having cartilage samples taken from other parts of the body.
Load More