University of Freiburg
-
Pine cones are pretty smart for things with no brains, enough so that scientists have copied them to create a unique window shading system. The setup blocks sunlight in the summer and lets it through in the winter, without using any electricity.
-
It’s hard to construct a building without a plan, but when did humans first start doing that? Archeologists have discovered the oldest known blueprints, with a 9,000-year-old rock carving in Jordan depicting a to-scale plan for a nearby megastructure.
-
In diabetics, wounds tend to progress quickly and heal slowly. Researchers have used electricity to heal diabetic wounds three times faster, which offers great potential for treating those with diseases that lead to reduced wound healing.
-
Researchers have developed a new type of artificial muscle that’s entirely made out of natural proteins. Responding to changes in its environment allows the muscle to flex on demand, which could make it useful for implants, prosthetics or robots.
-
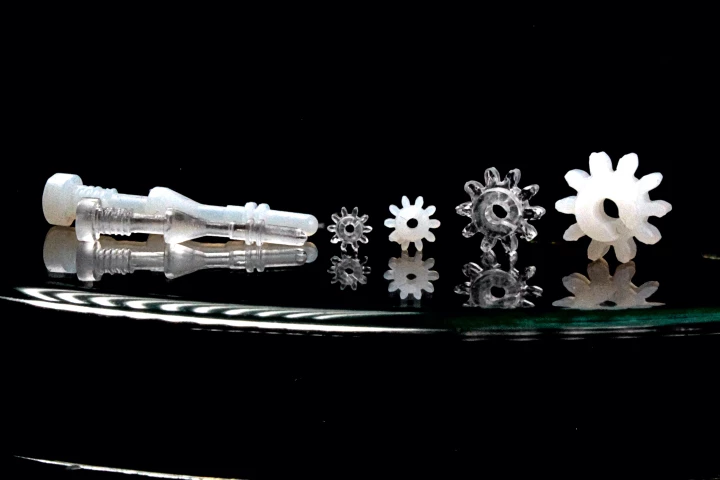
Plastic is a lot easier to work with than glass, which is one of the reasons it's used so much more often. That may be about to change, though, thanks to a new process that allows glass to be injection-molded – just like plastic.
-
Taking inspiration from the way sea cucumbers can strengthen their exterior when in danger, scientists in Germany have developed a novel wafer-thin paper material that can transition from firm to soft via an electrical switch.
-
A research team has demonstrated how using light to target specific brain cells, a technique called optogenetics, might work to tackle epilepsy, by using the approach to prevent seizures in mouse models of the disease.
-
Scientists in Germany have developed a technology that could give a waste product of the paper industry a new lease on life, converting the organic polymer lignin into the basis for a biopaste fit for 3D printing.
-
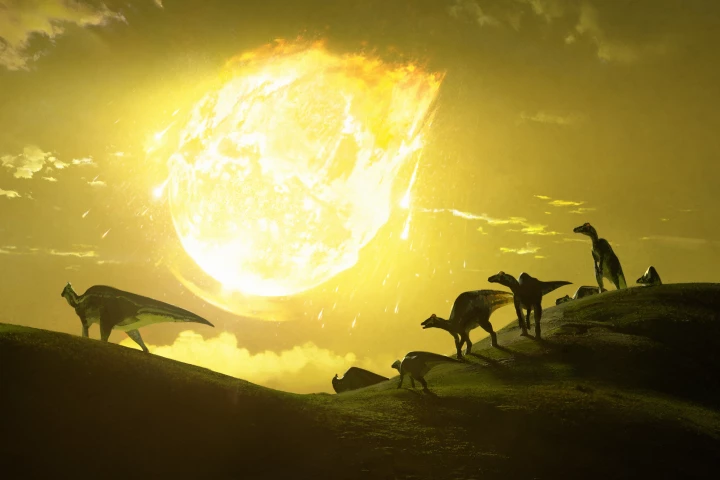
While a gigantic asteroid slamming into the Earth is never a sign of good luck, a new study has shown that the dinosaur-killing asteroid hit the planet at the deadliest possible angle, maximizing the devastating climate change that followed.
-
A new study exploring the potential for deep brain stimulation to treat severe depression has returned "absolutely sensational" results, with the reduction of depressive symptoms being not only fast-acting, but in some cases long-lasting.
-
Strong and light, spider silk is one of the most impressive materials in the natural world. Now, scientists in Germany and Switzerland have found a new use for spider silk – wrapping up cancer drugs to protect them until they can reach their tumorous targets.
-
To make water repellent coatings that are a self-healing, a team of scientists led by Jürgen Rühe at the University of Freiburg in Germany has come up with a superhydrophobic that sheds its outer skin like a snake to repair itself after being damaged.
Load More