Electromagnetic
-
With a single invisible shot, Raytheon's Coyote Block 3 UAV zapped swarms of drones out of the sky in a US Army demonstration showing that a reusable drone with electromagnetic weapons is an economical alternative to explosive interceptors.
-
The next frontier in unmanned aerial vehicle tech is all about keeping these aircraft fueled indefinitely. If we can crack it, drones could stay in the air longer, avoid landing to recharge, and carry on with their missions without interruption.
-
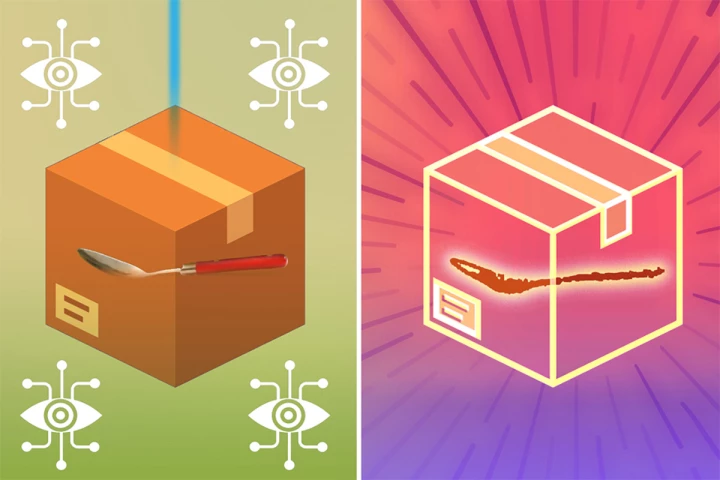
Researchers have developed a way to use high-frequency electromagnetic waves to visualize objects that are hidden from view – such as a tool in a pile of junk or a vase in a cardboard box – with much greater accuracy than before.
-
Drill bits are out, death rays are in. On May 21, 2025, New Atlas hit up Quaise Energy’s literal groundbreaking demo in Houston, Texas where a mm-wave maser melted rock to unlock the deepest, hottest, cleanest energy anywhere.
-
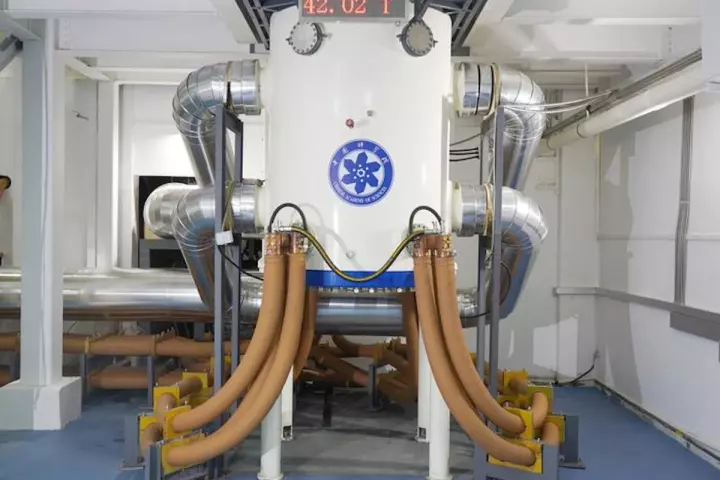
Scientists have developed the world’s strongest resistive magnet, which produced a steady magnetic field of 42 Tesla (T). The system could improve devices that use magnets, as well as enable a range of new experiments that probe electromagnetism.
-
In a move that echoes a sci-fi series, researchers have developed a material that was able to not only stimulate nerves in rodents, but reconnect them as well. The finding could lead to injectable particles that take the place of larger implants.
-
Taking a plot point from the 1990 Sean Connery movie thriller The Hunt for Red October, DARPA is working on a super-silent submarine drive that has no moving parts and provides propulsion through the water using magnets and electricity.
-
Researchers at Drexel University have created “Faraday fabrics” that can block almost all electromagnetic waves. The key ingredient is a 2D material called MXene, and the development could help protect wearables from interference and people from potentially dangerous radiation.
-
A research group at the University of Iowa has built what is described as a "remote control" for diabetes management that uses electromagnetic fields (EMFs) to reduce blood sugar levels and improve the body’s response to insulin.
-
Electromagnetic shielding is usually placed around electronics to prevent interference. Now, engineers have found that a 2D material called titanium carbonitride is excellent at the job, absorbing rather than reflecting electromagnetic waves.
-
Scientists at EMPA have developed a new aerogel-based material that blocks a wide range of electromagnetic radiation frequencies, forming what they describe as by far the lightest electromagnetic shielding material in the world.
-
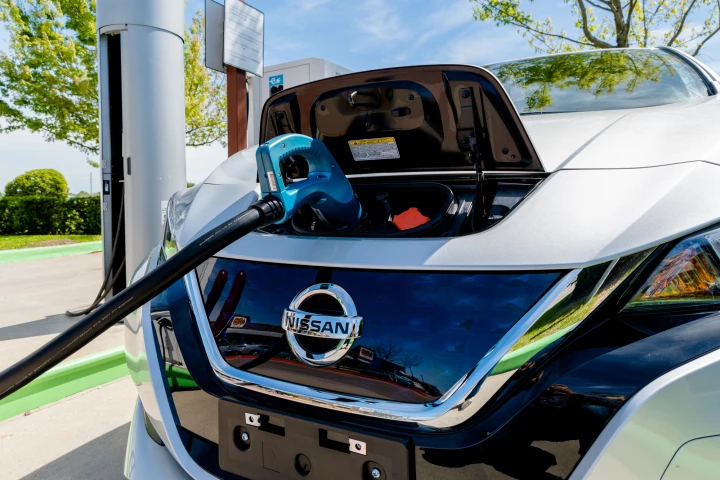
Although it doesn't happen often, it is possible for electromagnetic fields (EMFs) to affect the performance of cardiac implants such as pacemakers. Fortunately, though, a new study indicates that EMFs produced by electric cars pose no such danger.
Load More