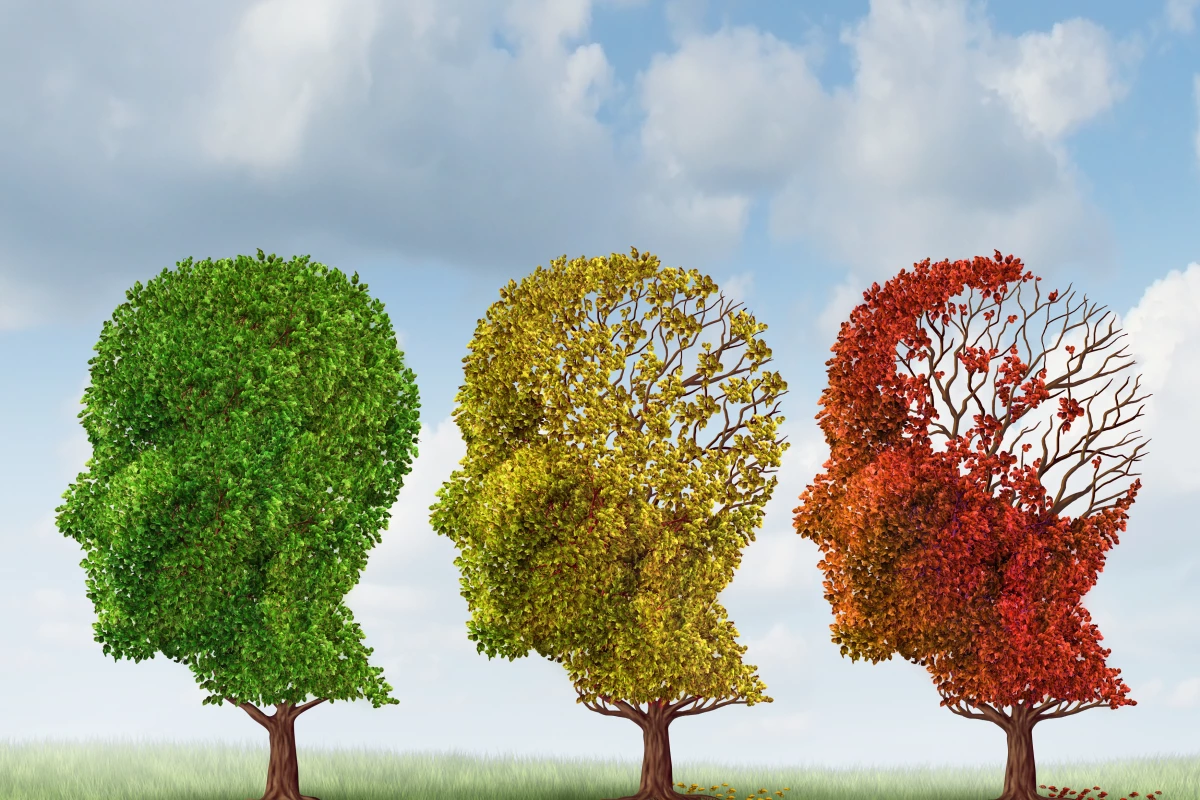
A team of researchers at Yale University has completed a molecular model for Alzheimer's disease by identifying a protein that plays a key role in its onset. Promisingly, the study showed that when the activity of this protein is blocked by an existing drug, mice engineered as models for human AD recover their memories.
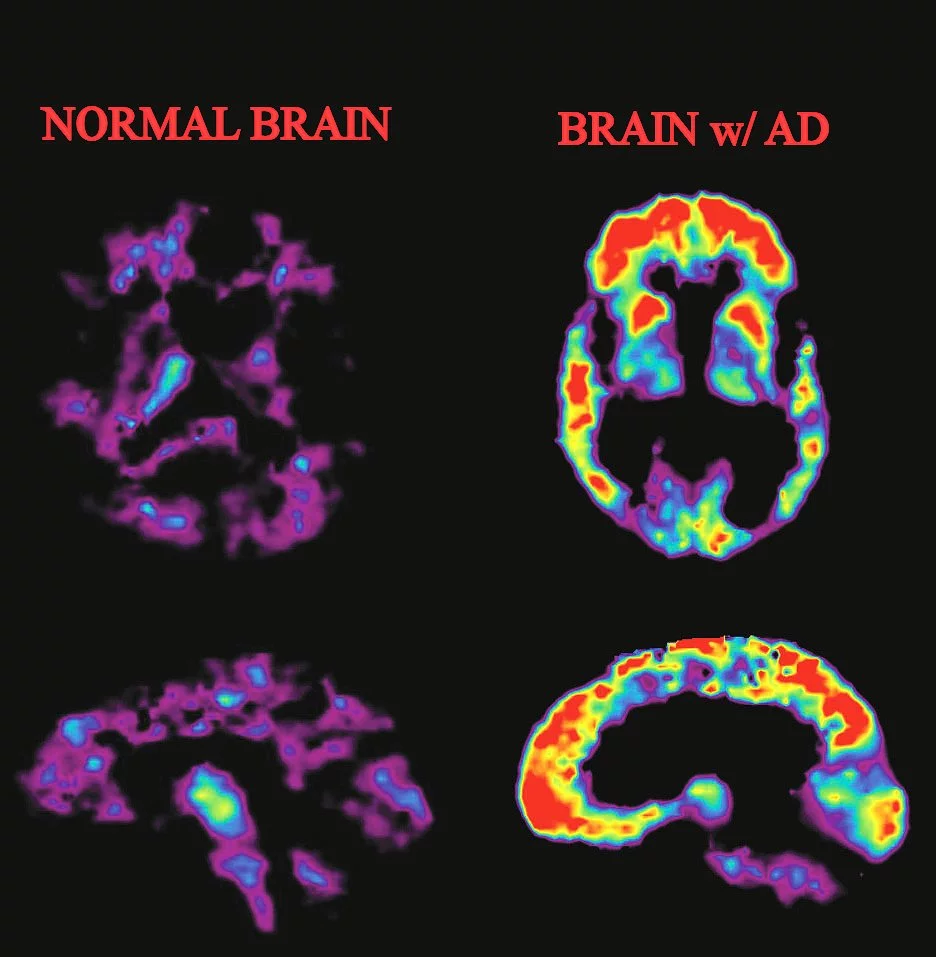
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a scourge of modern life, subjecting patients, families, and society to costs whose magnitude and nature are arguably unlike those of any other common disease. Often described as the progressive loss of self, more than 10 percent of those over 80 years in age are affected, a number projected to grow to about 100 million worldwide by 2050.
Alzheimer's disease has been a part of the human condition as far back as historians can gaze, although it was only identified as a unique combination of symptoms in the early 1900s. It wasn't such a major factor in everyday life in the past because life expectancy was much shorter, meaning people would tend to die prior to presenting with AD. For similar reasons, we have not evolved any very effective defense mechanisms against the advance of AD, either through evolution or through the progress of biology and medicine. While some progress has been made, developing a treatment without a clear understanding of the disease is a hard row to hoe.
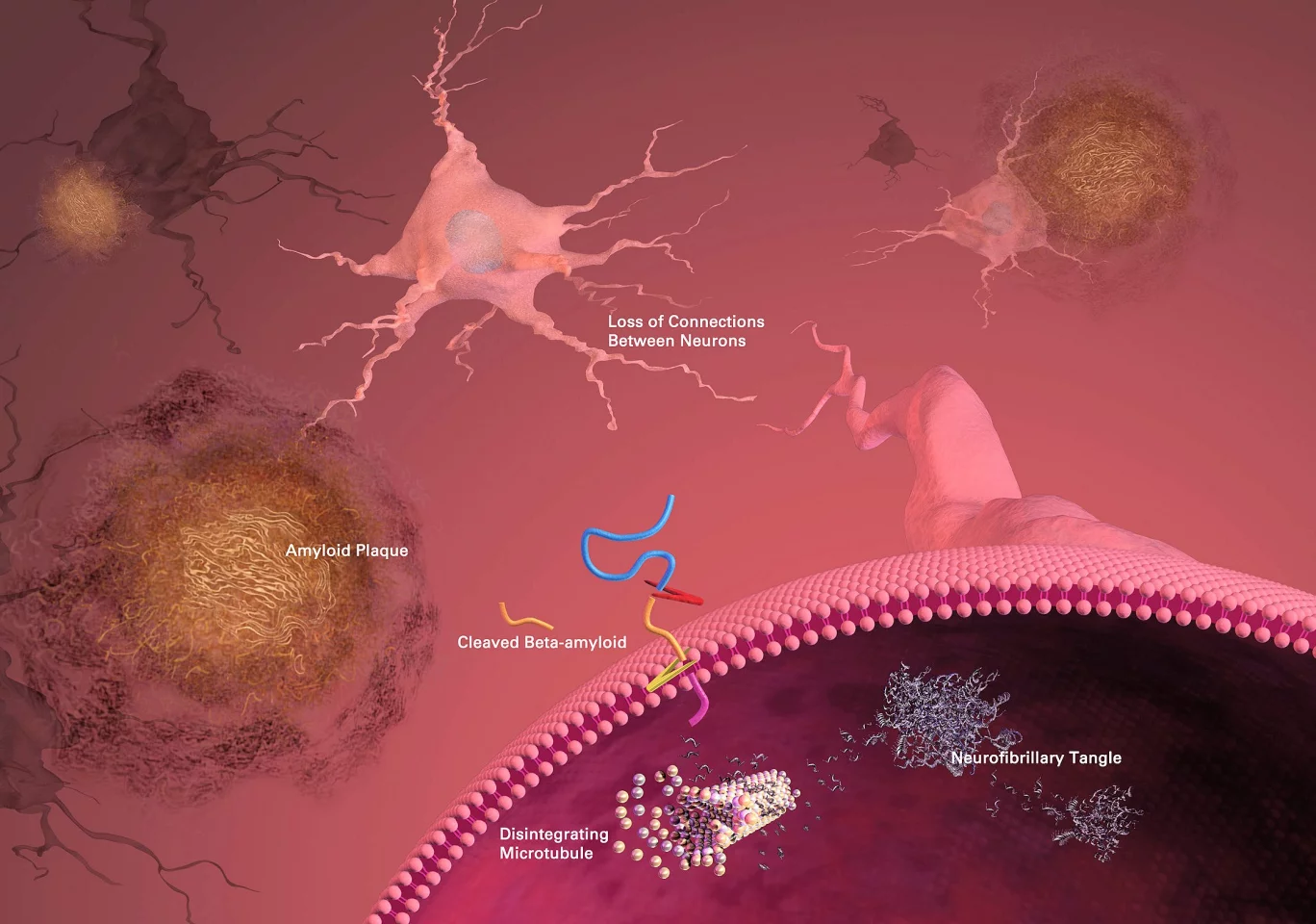
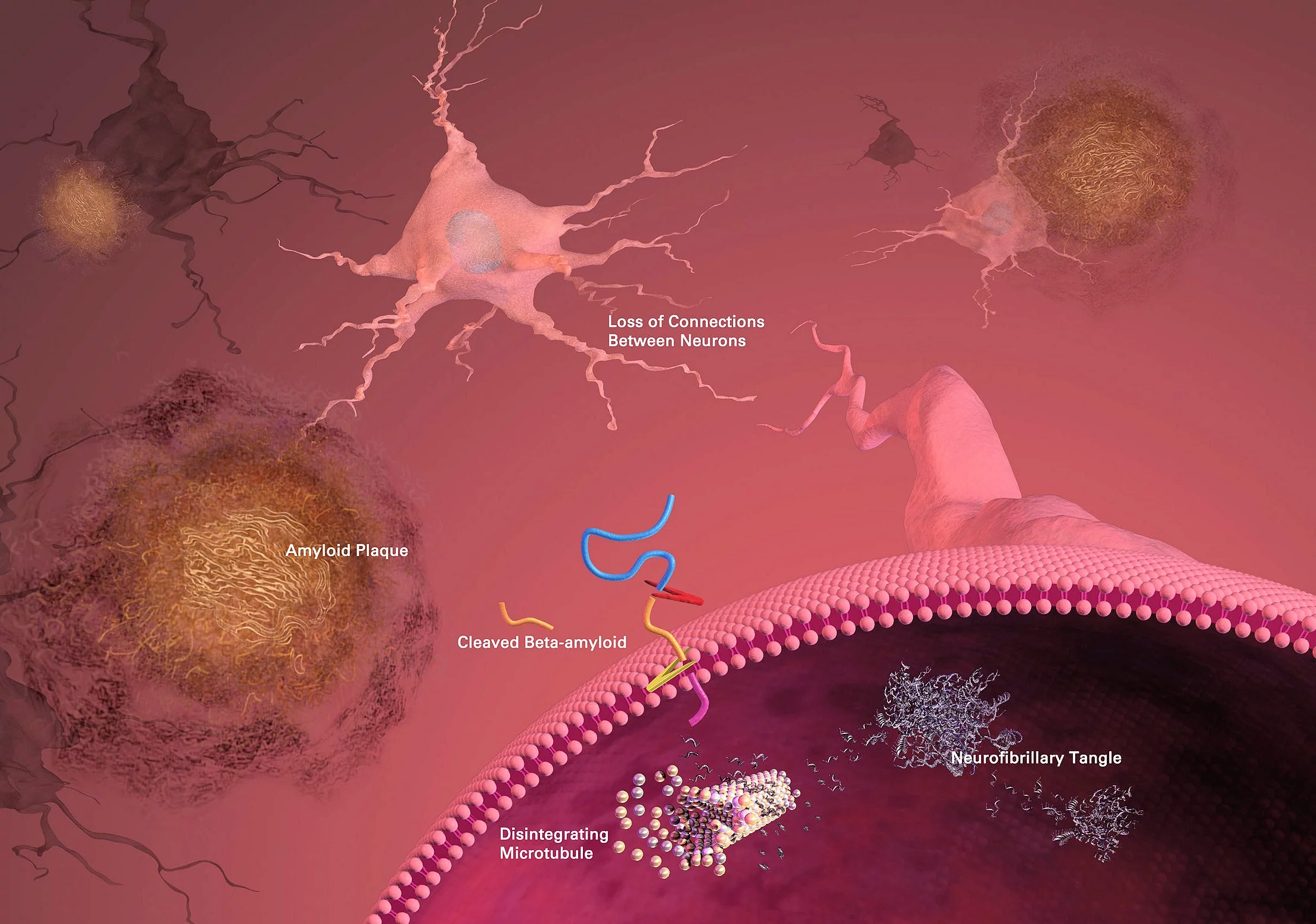
While there is as yet no generally accepted model for the cause or progression of AD, the two currently favored models both involve accumulation of abnormal proteins within the brain. The amyloid hypothesis suggests that accumulation of plaques made of a close relative of the beta-amyloid protein within the brain disrupts communication between neurons. This hypothesis includes a receptor that binds these plaques to the prion protein, which is connected with mad cow disease (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans.) However, lost function does not return when the plaques are simply removed from nervous tissue (e.g. by the immune system as stimulated by a vaccine), so they cannot be the whole story.
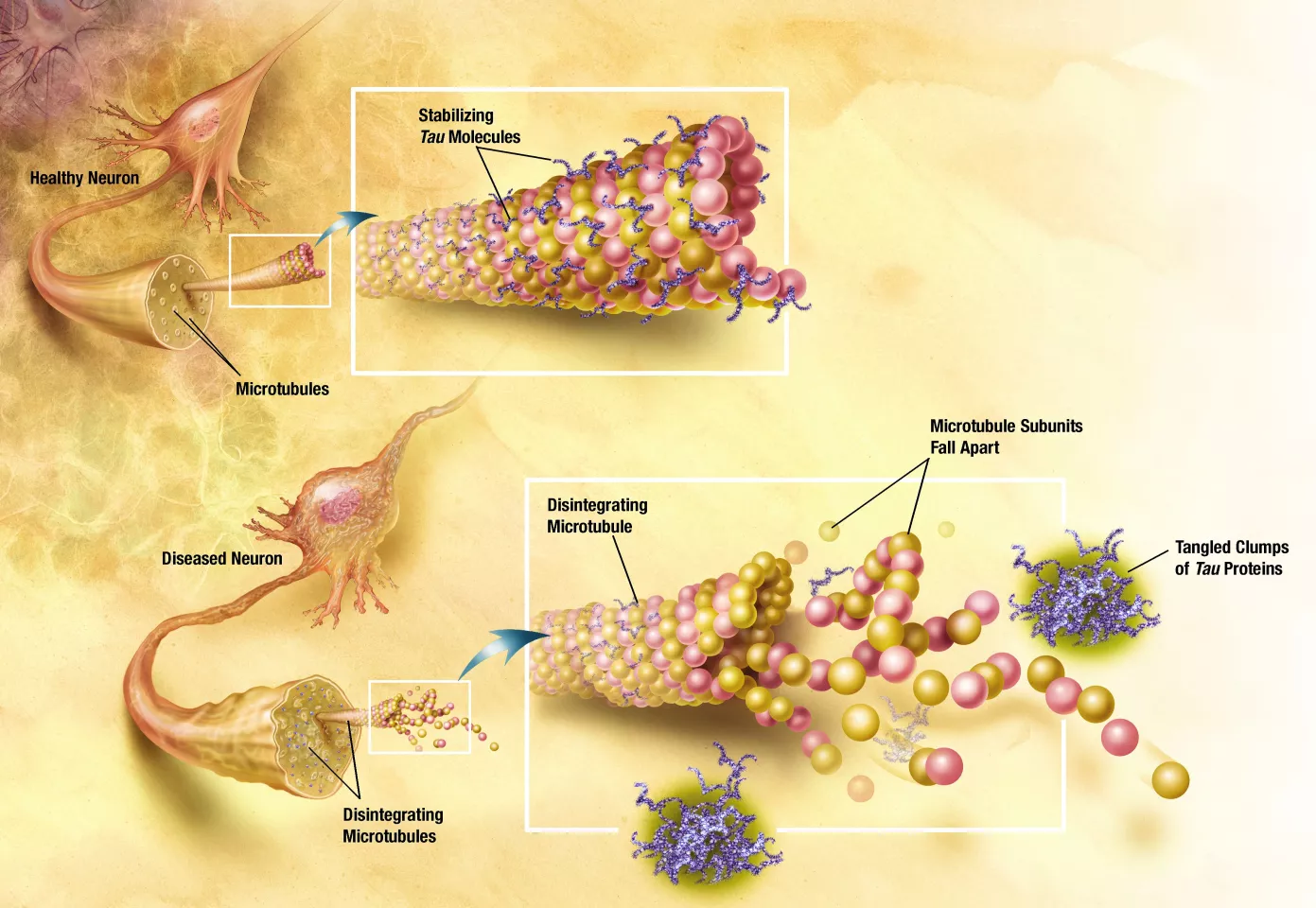
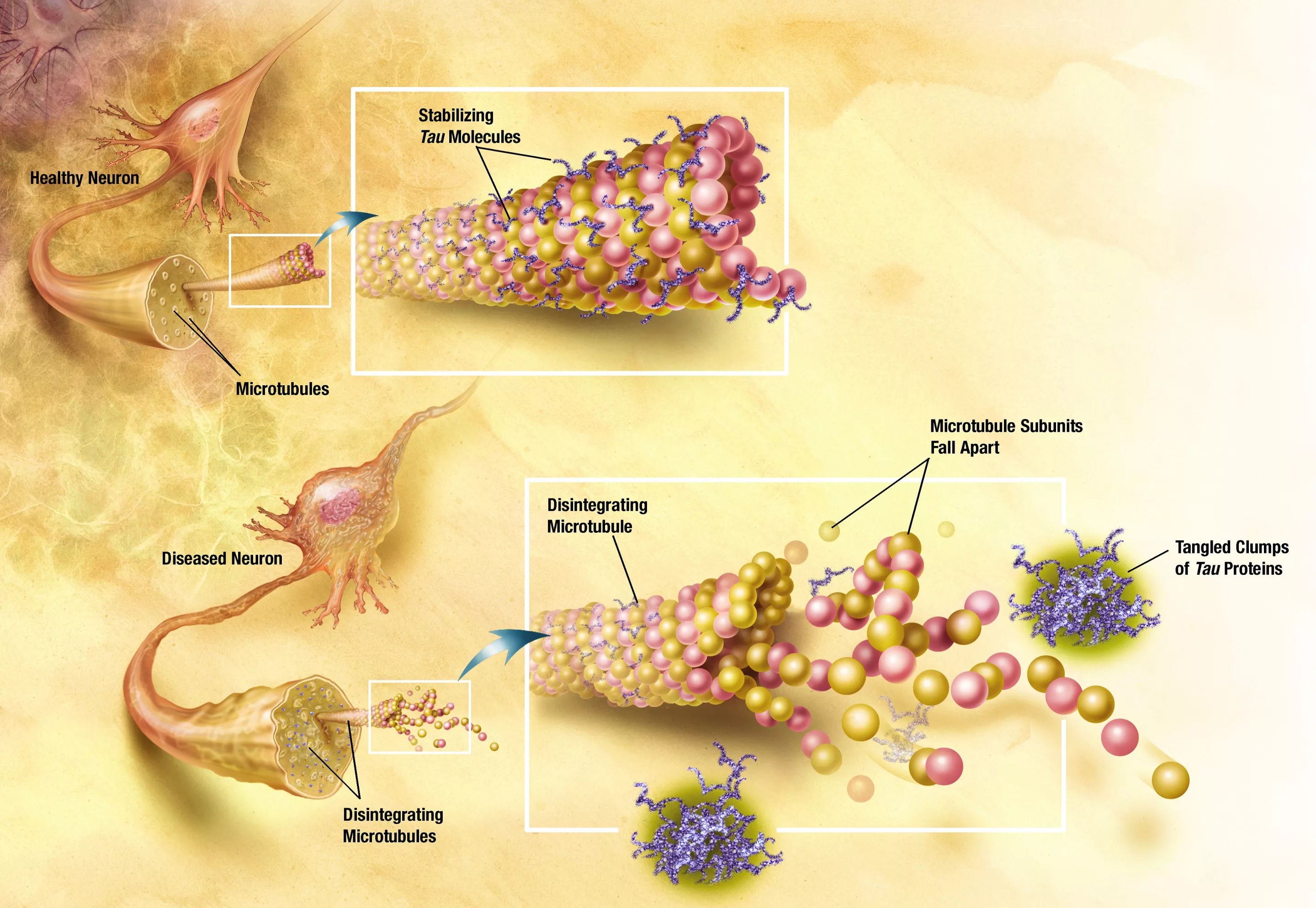
Tau proteins help stabilize the microtubules within the neurons of the brain against mechanical and chemical damage. The tau hypothesis for AD states that the tau protein can enter a state known as hyperphosphilation, in which the protein has acquired the maximum possible amount of phosphorous. At that point, they begin to spontaneously self-assemble into tangles of helical and straight filaments. Such tangles damage the structure of the neuron in which they form, diminish the functionality of individual neurons, and eventually destroy the cells themselves. Another potential difficulty associated with tau protein is that, if misfolded, it can lead to insoluble deposits which also damage the ability of the neurons to function. This again appears to link to the known prion diseases of the brain.
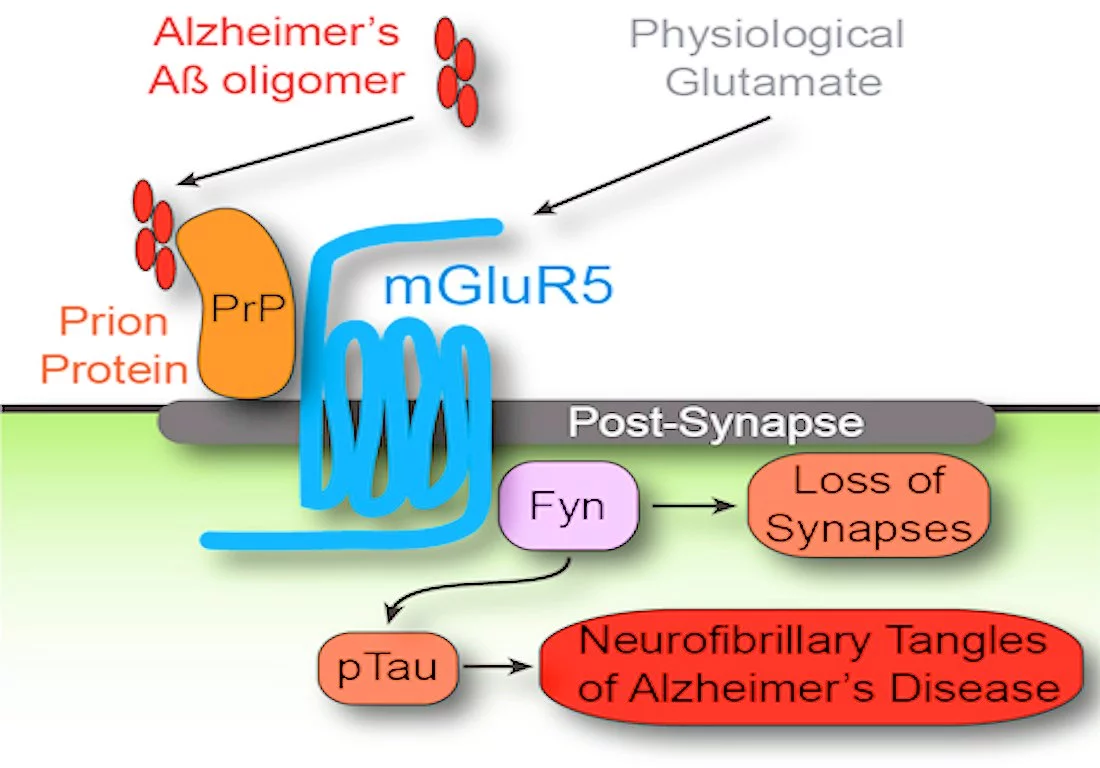
Yale professor Stephen Strittmatter's group, in an earlier study of the amyloid hypothesis, has shown that short segments of beta amyloid link up with prion proteins that reside on the cell membranes of the brain's neurons. In some then unknown manner, the linking of the amyloid and the prion protein led to the activation of Fyn, a signaling protein in cellular metabolism. In the end, this activation leads to the loss of synapses and tau protein tangles characteristic of AD.
In the most recent study (published in the medical journal Neuron) the Yale team reports the discovery that the activation of Fyn takes place through the mediation of a protein within the cell membrane, metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5). Antagonists and modulators of this receptor are known to have mood-leveling effects, and have been under investigation for use in patients with Fragile X syndrome, a genetic form of autism.
When such an antagonist drug was given to mice with AD-like brain damage, the ability of the mice to remember the past and set new memories for future access was restored. Inhibition of the mGluR5 signaling path proved far more effective in treating the underlying condition of the mice than did previous attempts to simply remove the plaques.
“What is very exciting is that of all the links in this molecular chain, this is the protein that may be most easily targeted by drugs,” said Stephen Strittmatter, the Vincent Coates Professor of Neurology and senior author of the study. “This gives us strong hope that we can find a drug that will work to lessen the burden of Alzheimer’s.”
There remains a great deal of work to carry out, first to discover if similar treatments will have analogous effectiveness on human AD patients, then to discover if such drugs are sufficiently safe for use in elderly patients. It is also not yet clear what level of damage might be reversed by mGluR5 antagonist treatment.
Even an extra year of mental clarity would no doubt be a great gift to those afflicted by Alzheimer's.
Source: Yale University